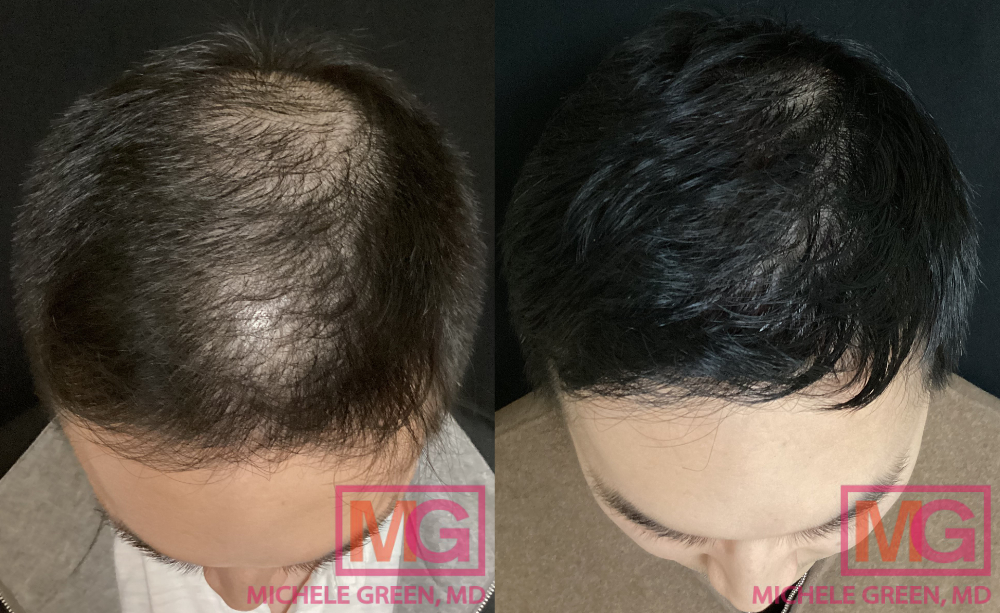
Hair Loss NYC
Dr. Green's Guide to Hair Loss & Hair Loss Treatment Options
Hair loss, thinning hair, and baldness can be devastating for both men and women. The key to successfully treating hair loss and hair thinning is to identify the underlying cause of your hair loss and address it appropriately. Dr. Michele Green is an expert in hair loss and has been at the forefront of innovation in treating thinning hair in NYC for over two decades. With the newest innovations, such as Platelet Rich Plasma injections (PRP) and Keravive™ HydraFacial for hair loss, Dr. Green incorporates the most cutting-edge technology in hair loss treatment for her patients. There are many medical conditions as well as genetic reasons that are the basis for alopecia or hair loss.
Platelet Rich Plasma, or PRP, is one of the most popular hair loss treatments offered in Dr. Green’s office, that entails collecting a sample of the patient’s blood, spinning it in the centrifuge to separate the plasma from the red blood cells, and injecting the plasma into the scalp to improve the health of hair follicles. This process helps encourage new hair growth and promotes increased retention, leading to decreased hair loss and hair thinning. When used with the right topical treatments, oral medications, and other innovative treatment modalities, PRP produces incredible results and thicker, healthier hair that lasts. Combining PRP with medications such as finasteride, minoxidil, and spironolactone can help effectively treat hair thinning and prevent baldness.
Dr. Michele Green was one of the first dermatologists in NYC to incorporate PRP into her practice and is consistently rated one of the best dermatologists in New York by Castle Connolly, Super Doctors, and New York Magazine for her evaluation, management, and treatment of the different types of alopecia in men and women. Dr. Green treats all types of hair loss, from androgenic alopecia to telogen effluvium to other autoimmune and hormonal causes of hair loss. Based in the Upper East Side of Manhattan, she is an internationally recognized expert for cosmetic and medical hair loss issues. When you consult with Dr. Green in her private dermatology office, you’ll have the opportunity to discuss your medical history, previous cosmetic treatments you may have had, and a thorough investigation of your concerns and cosmetic goals with her in-depth.
Dermatologist exams for hair loss in New York
There are many different causes why a male or female patient could lose hair, ranging from autoimmune, stress, hormonal issues, nutrition, metabolic, and genetic. If you are experiencing hair thinning or hair loss, the first step is to set up a consultation with a board-certified dermatologist like Dr. Michele Green. Dr. Green will begin her examination by first taking your complete medical history, which includes all of your past medical conditions, surgeries, travel, and medications. Next, she will examine your skin, hair, scalp, and nails to ascertain the reason behind your hair loss. Baseline photographs will be taken for your private medical record to track your progress during treatment.
Depending on the type of hair loss, a complete panel of blood work, including hormonal, autoimmune, and metabolic tests, may be ordered to help confirm and identify the etiology of your hair loss. The skin and scalp, as well as the hair itself, can explain why your hair is thinning. A biopsy or fungus culture of the scalp, skin, nails, or the hair itself may be needed to arrive at the correct diagnosis for your hair loss and formulate the best treatment plan. Alopecia can be a complicated issue, and a complete analysis must be performed to ascertain the causes of hair loss.

3 months before and after injections for hair loss
What is the hair growth cycle?
Hair loss is a very prevalent concern for both men and women. The American Academy of Dermatology notes that over 80 million Americans suffer from some form of hair loss. Since the advent of COVID-19 (Coronavirus), there has been an increased number of hair loss cases in the United States. Hair loss can occur anywhere on the body, but the most common place to be affected is the scalp. The hair growth cycle occurs in three discrete phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen. The first phase, known as the anagen phase, makes hair grow actively. The anagen growth phase lasts from 2 to 6 years. Most of the hair on your scalp is in the anagen phase. During this phase, the hair follicle grows a new hair shaft. The next phase, known as catagen, lasts about ten days. The final phase of telogen lasts for two to three months, at which time the follicle rests, and later, the hair falls out, and the cycle is repeated. A typical amount of hair loss is between 50 to 100 hair strands per day as the hair goes through this growth cycle. Changes or disruptions in this hair growth cycle, or damage to the hair follicle, is what causes alopecia or observed hair thinning and hair loss. Dr. Michele Green is an expert in NYC who identifies the causes of this hair growth disruption and uses the best treatments for your hair loss.
What are the common causes of hair loss?
There are many reasons for hair loss, from more common types to rare genetic ones. The following outline is a complete list of the more common causes of hair loss:
- Genetics
- Hormonal such as thyroid disease, hypothyroidism
- Polycystic Ovary Disease (PCOS)
- Stress
- Severe illness with fever, such as COVID-19 (Coronavirus)
- Poor nutrition, such as vitamin deficiency or mineral deficiency
- Pregnancy
- Childbirth
- Puberty
- Menopause
- Medications
- Bacterial infection
- Fungal infection
- Lupus
- Lichen Planus
- Secondary Syphilis
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Hairstyles
- Autoimmune disease
- Radiation therapy
- Extreme weight loss
- Anorexia
- Trichotillomania
Is Hair Loss Genetic? Is Hair Loss hereditary?
There are genetic components that contribute to hair loss, and it has been observed to run in families. Several other contributing factors, including hormones, aging, underlying health conditions, hair styling, illness, and more, may also influence hair loss. Androgenic alopecia, which is more commonly referred to as either male-pattern hair loss or female-pattern hair loss, is a hereditary condition. Hereditary hair loss typically becomes more noticeable with age. Genetic hair loss often presents in a predictable and identifiable pattern. In male-pattern hair loss, the first noticeable loss typically presents as a thinning crown and receding hairline that creates an “M” shape. Female-pattern baldness typically presents as diffuse thinning and a wider part. Although hereditary hair loss can not be entirely prevented, it can be significantly delayed when patients take advantage of various treatment options. A board-certified dermatologist, such as Dr. Michele Green in NYC, can recommend a combination of the best topical serums, oral medications/ supplements, in-office procedures, and other treatment options for delaying hereditary hair loss and keeping your hair thicker, healthier, and fuller for longer.
What are the different types of hair loss?
- Androgenetic alopecia, which includes both male and female pattern hair loss
- Traction alopecia
- Telogen Effluvium
- Anagen Effluvium
- Loose Anagen Syndrome
- Alopecia Areata
- Tinea Capitis
- Cicatricial Alopecia: including Lichen Planopilaris, Discoid Lupus Erythematous, Folliculitis Decalvans, Dissecting Cellulitis of the scalp, Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia
- Hair Shaft Abnormalities
- Hypotrichosis
- Trichotillomania
How much hair loss is normal?
According to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), the average person loses anywhere from 50 to 100 strands of hair daily. The hair will continue to shed as part of the hair’s natural cycle. If you are concerned with the amount of hair loss, it is best to count the amount of hair you lose in one day, including on your brush or in the shower, to ascertain if it is normal. Genetics and hormones dictate the rate of hair growth. Generally, hair grows a millimeter per day, with an annual hair growth of approximately six inches. If you feel that you are losing an excessive amount of hair or your hair is growing at a decreased rate, it is time to consult with a trained dermatologist like Dr. Green.
Treatment Options: Hair Loss Treatment in NYC
- The treatment options for hair loss depend on the types of hair loss you suffer.
- Finasteride (Propecia) is an FDA-approved drug for treating androgenetic alopecia (male patterned baldness). DHT (dihydrotestosterone) is a male androgenic hormone that shrinks hair follicles. Propecia is a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor, which helps reduce hair loss by blocking the action of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This shrinkage of the hair follicles ultimately leads to hair loss and baldness. Propecia is effective in treating both men and post-menopausal women with hair loss. Propecia is a lower-dose version of the medication Prosper, used to treat male prostate hypertrophy. Finasteride works by lowering the DHT levels in the body slows hair loss and promotes new hair growth. Duasteride, marketed as Avodart, while approved to treat prostate hypertrophy, is used off-label to treat hair loss.
- Spironolactone is an FDA-approved prescription medication that treats androgenetic alopecia and PCOS in women by slowing the production of male sex hormones (androgens). It is also used for females with hair loss due to hormonal imbalances, as it works by obstructing the androgen (male hormone receptors), which control the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and testosterone levels. These levels can lead to different degrees of hair thinning or permanent hair loss.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine) is an FDA-approved topical treatment for hair loss. Minoxidil comes both as a solution and as a foam base, which needs to be applied to the scalp at bedtime. Minoxidil can be used to complement PRP hair treatments and can be used long-term to sustain the results achieved from PRP.
- Hair Vitamins, especially B vitamins such as biotin, are especially useful in treating hair loss. Dr. Green recommends Viviscal and Nutrafol for hair growth.
- Viviscal is a supplement formulated with essential vitamins such as Biotin, Vitamin C, and B Vitamins, in addition to other proprietary vitamins that have been clinically proven to thicken and help hair grow.
- Nutrafol is a proprietary blend of vitamins clinically proven to restore hair growth. It is available both as an oral vitamin supplement and a topical vitamin-enriched solution. The vitamin and nutrient formulation in Nutrafol, such as saw palmetto, prevents the conversion of the male androgen hormones into DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which is responsible for baldness.
- Hormone Replacement therapy is reserved for patients who have lost hair secondary to menopause, PCOS, or hormonal irregularities.
- Stress Reduction – Stress causes hair loss in many situations, and reducing stress has a positive influence on hair regrowth.
- PRP injections – PRP injections, for both men and women, are extremely effective for many different types of hair loss, including androgenetic alopecia.
- Exercise -It has been documented that exercise reduces stress, creates endorphins, and helps maintain positive hair growth.
- Hairpieces—Hair replacement techniques, including wigs, hairpieces, and hair weaves, can also help disguise hair loss.
- LaserCap—Many patients with male and female pattern baldness benefit from LaserCap. Used three times a week for 30 minutes, it helps maintain and restore hair growth. Its effective low-level laser therapy (LLLT) re-energizes inactive hair follicles. The LaserCap is an excellent adjuvant treatment for maintaining hair growth.
- Nutrition—Good nutrition is essential for proper hair growth. Extreme dieting or a poor diet can influence hair thinning and shedding.
- Hair Products—Using the right shampoos, conditioners, and serum can help protect hair from damage.
- HydraFacial Keravive – can help stimulate circulation in the scalp and stimulate hair follicles to grow. It can be used with male and female pattern baldness and Telogen Effluvium.
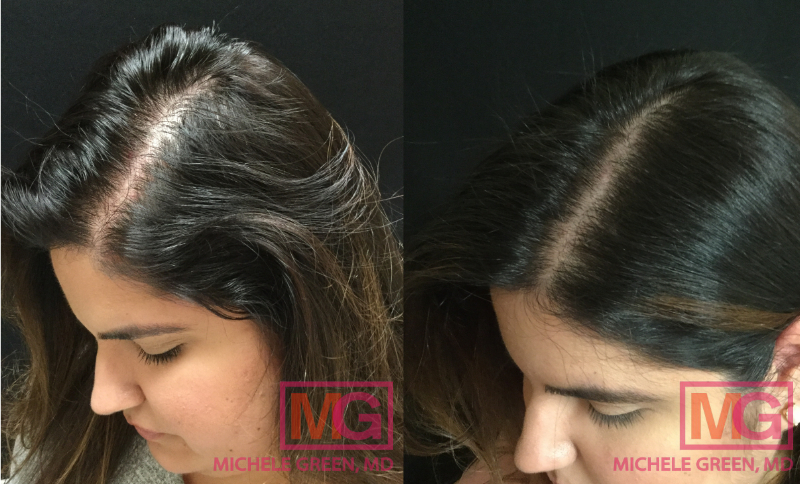

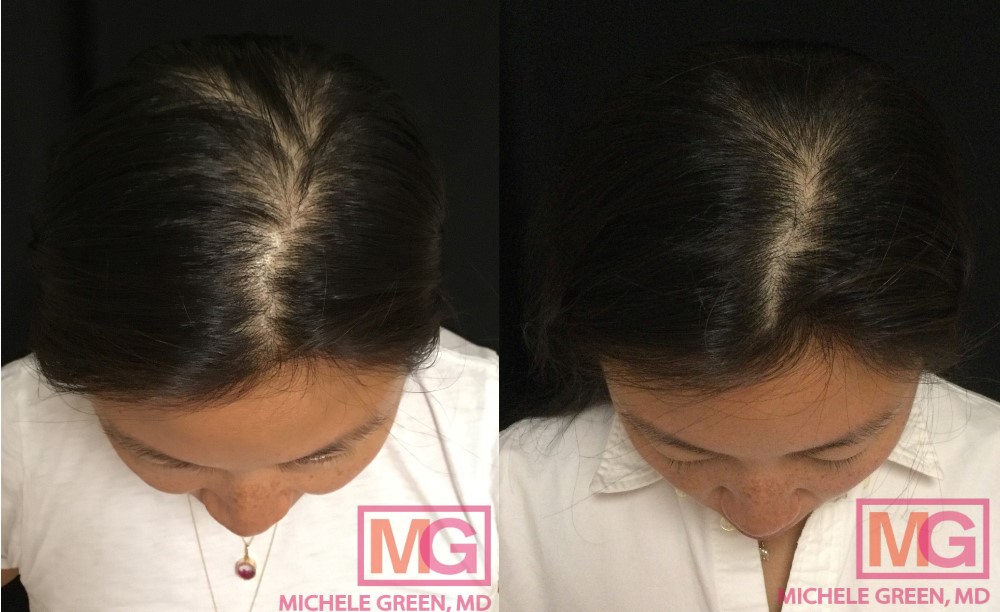
37 year old female, PRP to scalp for hair loss – 6 months
Why is Oral Minoxidil Effective for Hair Loss Treatment?
Oral Minoxidil was originally FDA-approved to treat hypertension and high blood pressure. In recent years, studies of low-dose oral Minoxidil have demonstrated that it can be effective in preventing and treating both male pattern and female hair loss. Topical minoxidil is also effective for treating hair loss but can be irritating or frustrating in terms of daily application. Dr. Green often prescribes oral minoxidil, which improves blood flow to the scalp to strengthen and thicken the hair follicles for improved hair growth. The majority of people who try oral minoxidil find that the treatment reduces shedding or leads to decreased hair loss. Oral minoxidil can be used to treat both male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness effectively.
Finasteride to Treat Hair Loss
Finasteride is a DHT (dihydrotestosterone) blocker that helps to prevent and treat hair loss. Also known by the brand name Propecia, Finasteride is a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor, meaning that it binds to the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme to prevent the conversion of free testosterone into DHT. DHT can contribute to the development of male-pattern baldness, as the hormone binds to hair follicles, damaging them and preventing healthy hair growth. Patients who are prescribed Finasteride can take the medication in the form of a pill once a day.
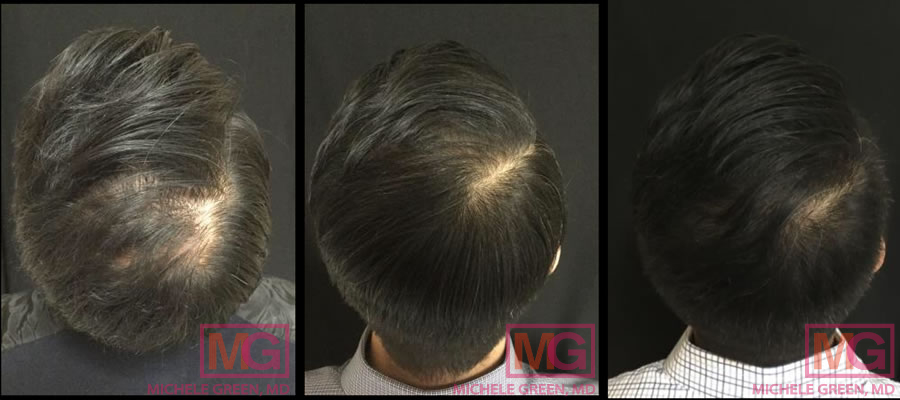

Male 35-44 years old, PRP treatments 3 and 10 months after
Androgenetic alopecia: female-pattern hair loss and male-pattern baldness
Androgenetic alopecia is the most common type of hair loss that is treated in dermatology. It is often referred to as male pattern baldness in men and female pattern hair loss in women. This type of hair loss affects more than 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States. In androgenetic alopecia, the anagen, or growth cycle, becomes shorter, and the hair follicles make progressively thinner hairs. This type of hair loss is typically hereditary, and the observed hair loss is generally a gradual process. In men, the classic pattern of hair loss occurs in the temporal areas, receding hairline, and bald spots in the crown or on top of the head. Male pattern hair loss is caused by androgen-mediated follicular miniaturization. This is due to a sensitivity to the male hormones called androgens. In women, generally, diffuse thinning occurs around the crown area and the anterior portion of the scalp. Women do not experience the horseshoe baldness that occurs in men; instead, the entire crown may experience diffuse thinning. In female-pattern baldness, the scalp hairs become progressively thin, and women may first notice this hair loss when trying to part or comb their hair.
What causes balding in males?
In the past, the loss of hair in men was accepted and attributed to the genetics of male pattern baldness. Although a family history of hair loss does affect one’s ability to retain hair, it is not the only contributing factor. Men with hereditary hair loss generally follow the typical male pattern, which is receding hairline at the anterior hairline and thinning at the top of the head, creating the characteristic “M” shape to the hairline. A decrease in testosterone and hormonal changes all lead to an increase in hair loss and balding in men. Male-pattern baldness affects as many as 50 million men in the United States, making it an incredibly common condition, which tends to become more apparent with age. Luckily, Dr. Green has many solutions available to reduce hair thinning and balding due to male-pattern baldness.
Treating Male Pattern Baldness NYC
Thanks to recent advances in dermatology in treating hair loss, we understand that male pattern baldness is not an eventuality. There are many ways to prevent this hair loss cycle in men, such as combating shedding and re-growing hair. One of the most effective and exciting treatments that can be used to combat male pattern baldness is platelet-rich plasma (PRP). PRP is a practical solution when looking for a natural method for stimulating hair growth. PRP injections are a revolutionary treatment that stimulates new hair growth in men who suffer from androgenetic alopecia. PRP treatment works by using your blood cells to extract the growth factors that stimulate hair growth. In addition to PRP, there are several alternative options available for treating male pattern baldness, including oral medications such as Propecia or finasteride, along with topical treatments such as Minoxidil (Rogaine). Dr. Michele Green is a firm believer in a proper diet, exercise, nutrition, and vitamin supplements, such as Nutrafol and Viviscal, to help re-grow hair. Dr. Green also recommends the LaserCap RX, an FDA-approved prescription laser cap for hair regrowth. The LaserCap uses low-level laser therapy to promote hair growth in the comfort of your own home.

What causes hair loss in females?
Female pattern baldness may indicate a more serious underlying health concern. Dr. Green will do a thorough history and examination to reveal the etiology of your hair loss. Female hair loss may be due to a myriad of symptoms. Some women suffer from hormonal changes such as hypothyroidism, PCOS, menopause, poor diet, nutritional deficiencies, autoimmune diseases, or stress. Female pattern hair loss can even result from a side effect of certain oral medications. Other signs of hair loss may be associated with eczema, psoriasis, lichen planus, or lupus erythematosus. Female-pattern baldness typically starts with scalp hears, particularly in the front, becoming less dense. Some women first notice it when they are parting their hair or styling it.
Treating Female Pattern Baldness NYC
To find the best treatment for female pattern baldness, which is characterized by hair loss along the hairline in females, Dr. Green will start by examining the treatment area. A blood test or scalp biopsy may be necessary to make a complete diagnosis. One treatment proven to work well in cases of female pattern baldness is Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) – this non-surgical approach uses a patient’s blood cells injected into the scalp to initiate hair re-growth. PRP is highly effective and is one of the main treatment options Dr. Green recommends to her New York City patients due to its impressive hair growth results.
Alopecia Areata and Hair Loss
Unlike more common forms of hair loss, alopecia areata is a more sudden and unpredictable hair loss issue that starts with one or more circular, non-scarring areas of patchy hair loss or bald patches. Alopecia areata can affect both adults and children. Non-scarring alopecia results from the reduction or slowing of hair growth without damaging the hair follicle. There are several different causes of non-scarring alopecia, including alopecia areata, androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern hair loss), stress or medications as in (telogen effluvium) psoriasis, or fungal infection of the scalp (Tinea Capitis), among other reasons.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease and affects approximately 6.8 million people in the United States. In alopecia areas, the body’s immune system attacks your healthy tissues, including your hair follicles. It usually begins as hair loss in just one or two areas of patchy hair loss on the scalp, the size of a quarter. The area of alopecia can appear in other areas of the body or face, such as the eyebrows or beard area. Alopecia areata may progress to total loss of all hair on the scalp and complete baldness, which may lead to alopecia totalis as well as complete hair loss on the body (alopecia universalis). Both men and women can be affected by this disease, and most cases occur in younger patients before 30 years of age. There is a strong genetic component to alopecia areata, and there is anecdotal evidence that stress can contribute to this condition. Some patients recover and re-grow hair spontaneously, while others progress to have complete hair loss. Dr. Green uses a combination of topical therapies, PRP for hair loss, and intralesional cortisone treatments for patients with alopecia areata to re-grow their hair.
Is there a cure for Alopecia Areata?
There is currently no cure for alopecia areata. However, many treatments are available to keep it under control, help restore hair loss, and prevent its spread.
- Intralesional cortisone injections—The most common treatment is intralesional corticosteroid injections directly into the areas of hair loss. If these patches of hair loss are treated early, they seem more responsive to the positive effects of the injections.
- PRP injections—Injections of platelet-rich plasma encourage hair growth since they are replete with all of the growth factors that occur naturally in the body.
- Topical Minoxidil (Rogaine)- Minoxidil stimulates new hair growth and helps maintain the current hair thinning or shedding.
- Anthralin (Dritho-Scalp) – is a topical medication used to control inflammation at the base of hair follicles. It is an artificial version of a natural substance found in goa powder, which is from the araroba tree.
- Olumiant (baricitinib) is the first oral tablet approved by the FDA in June 2022 to treat adult patients with severe alopecia areata. It is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor that blocks the activity of one or more enzymes, allowing it to interfere with the mechanism that causes inflammation.
Will stress cause hair loss?
Many patients wonder, “Can stress make you lose hair?” and the answer is that three types of hair loss are associated with stress. They are Telogen effluvium, Trichotillomania, and Alopecia Areata. With Telogen effluvium, stress causes the hair follicles to become dormant (enter a resting process), and after three months in the resting period, the hair falls out. This stress results in reduced hair growth and thinning. The stressor event, such as a fever, surgery, or other illness, can induce between 20 to 50 percent of scalp hairs to transition into the telogen phase before the hair falls out. Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks its hair follicles. Trichotillomania is an uncontrolled and impulsive disorder of pulling one’s hair, which results in the hair being pulled from the follicle. It can take six weeks to six months for hair loss to occur from a stressful event. Stress-related hair loss can be permanent if not treated in its early stages. In some cases, there can also be scar-related issues such as cicatricial alopecia – where damaged skin may impact hair growth or prevent the regrowth of new hair.
If you’ve noticed that your hair is thinning or excessively shedding, it is important to contact an expert in hair loss, like Dr. Michele Green, immediately. Getting treatment for hair loss in its early stages, before bald spots appear, can help minimize overall hair loss and increase the odds of a treatment’s efficacy. Hair loss can seem overwhelming, so it is necessary to consult with a trained dermatologist, like Dr. Green, who will assess your condition and explain all of your treatment options.
Which medications cause hair loss and thinning hair?
All too often, the very medications we are taking to treat one medical condition can cause unexpected hair loss or problems with hair growth. The following types of medications have been known to exacerbate or cause hair loss:
- Blood Pressure Medications (beta blockers and ACE inhibitors) like captopril, lisinopril, and metoprolol have all been reported to cause hair loss in one percent of patients who take them.
- Chemotherapy drugs- can cause an anagen effluvium and affect the hair of the scalp, eyelashes, eyebrows, and body.
- Antidepressants – such as Paxil, Zoloft, Elavil, and Prozac have been associated with hair loss.
- Antibiotics – can cause a decrease in vitamin B and hemoglobin, which causes decreased hair growth.
- Cholesterol-lowering medications such as atorvastatin (Lipitor) and simvastatin (Zocor).
- Psoriasis treatment – Acitretin
- Acne medication – Accutane (Isotretinoin) is used to treat cystic acne.
- Weight loss drugs – Phentermine can cause hair loss.
- Gout medications – such as allopurinol (Zyloprim and Lopurin), have been known to contribute to hair loss.
- Anticoagulants – such as Warfarin (Coumadin)
- Birth Control Pills – while some birth control pills can help treat hair loss, they can cause hair loss in other patients.
- Anti-arrhythmia drug – Amiodarone (Cordarone) has a rare side effect of hair loss.
- Antacids – like Cimetidine (Tagamet), cause hair loss.
- Testosterone – Excess testosterone in female patients can lead to hair loss, and a lack of testosterone in men (due to taking anabolic steroids for extreme weight lifting or muscle building) can cause hair loss.
- Anti-fungal medications – such as Ketoconazole, have been described to cause hair loss.
- Immunosuppresants – such as methotrexate, cychophosphamide (Cytoxan) and etanercept (Enbrel) all can cause hair loss.
Menopause and Hair Loss
Menopause has many side effects, including hair loss and thinning, which are distressing. As a consequence of menopause, estrogen levels decrease, and testosterone levels rise. Since estrogen is the hormone most responsible for hair growth, the fall in estrogen levels causes hair shedding and thinning. In women, hair can slowly begin to thin all over the scalp. The hairline is usually stable. Simultaneously, the increase in testosterone levels also interferes with hair growth. The combination of the changes in both hormones causes hair to become thinner and women to lose volume and luster. At the same time, the rise in testosterone contributes to the thinning of your hair and the increased growth of facial hair. There is, of course, a gradual thinning and loss of hair that comes with age, called involutional alopecia. To treat the hair loss caused by menopause, proper nutrition, exercise, PRP injections, hair vitamins, LaserCap, and hormonal replacement therapy may be necessary to reverse the hair loss. In severe cases, a hair transplant may be an effective solution.
How Does Pregnancy Affect Your Hair?
During pregnancy, many women experience changes to their hair, both in terms of growth and texture. Generally, the hormones associated with pregnancy will thicken your hair, grow faster, and have less shedding. Increased nutrients are brought to your hair and nails during pregnancy due to increased metabolism. However, after delivery, both the texture of your hair and your growth rate return to normal. From several days to months after delivery, postpartum hair loss can occur.
When does postpartum hair loss stop?
Postpartum hair loss can begin immediately after delivery. The hair that might have been shed while pregnant may start to fall out. This shedding can last up to one year but is generally at its peak in the fourth month after delivery. Continued use of prenatal vitamins can help mitigate some of this hair loss, as well as a healthy diet, rest, and exercise.
Tinea Capitis
A superficial fungal infection of the skin, scalp, or eyebrows causes Tinea Capitis. The infection, also called scalp ringworm, typically attacks the hair follicles of the scalp. Initial symptoms may be dry, pruritic, red scaling patches that appear almost like dandruff. Over time, the hairs are broken off at the scalp surface, leaving you with smooth areas of hair loss. A typical pattern of hair loss is in a “moth-eaten” distribution. Over time, if left untreated, hair loss progresses, and a kerion can develop.
Children who are affected may develop sores or blisters that ooze on the scalp and even develop fever and associated swelling of the lymph glands. A kerion can develop, which is an extremely inflamed mass and appears as an abscess. Tinea Capitis must be identified rapidly to prevent the spread of this fungal infection. A fungus culture of the hair and its root can provide the correct identification of the fungus. Oral and topical fungal medicines are needed to remediate this contagious condition. Tinea Capitis is more common in younger children than adults and needs prompt medical diagnosis and treatment.
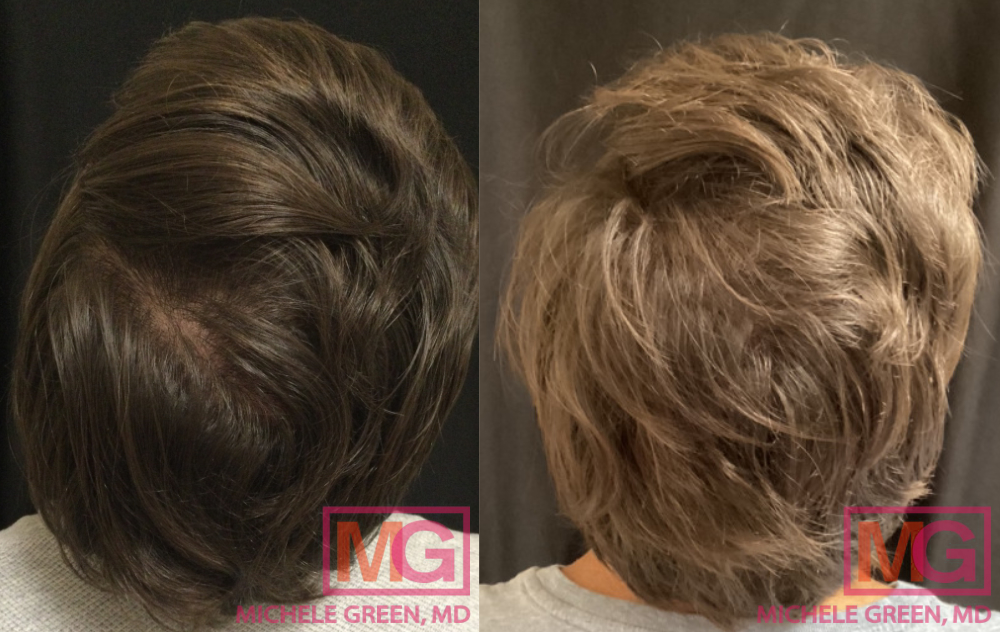
PRP treatment, 2 months before and after
Traction Alopecia
Traction alopecia is a form of alopecia caused primarily by tightly pulled hairstyles. Typically, traction alopecia is seen in patients who wear their hair too tight in ponytails, buns, hair extensions, weaves, cornrows, dreadlocks, or braids. The main symptom is missing or broken hairs, especially along the front of the hairlines or sides of the scalp. Typically, patients notice a receding hairline around the forehead, temple, or nape of the neck, where hair styling causes hair loss. There may be irritation, redness, itching, ulcers, or pimples in this area as well. The appearance of the scalp can be that of an infection of the scalp or folliculitis.
If traction alopecia continues, the hair loss and thinning hair can become permanent since the hair follicles become so scarred that new hairs cannot form. Traction alopecia is common in ballerinas and gymnasts who wear their hair in a tight bun daily for their profession. This condition is also common in African American patients due to hairstyles, such as braids or cornrows, which are too tight. Any individual of any ethnicity can suffer from traction alopecia. The older you are, the more vulnerable you become to having permanent hair loss from traction alopecia.
To avoid traction alopecia, it is best to wear your hair loose and avoid constricting hairstyles that will pull your hair. In addition to hairstyles, it is best to coif styling devices like hot rollers or hair straighteners. It is also best to limit the amount that you chemically process your hair, use flat irons, excessive heat, weaves, extensions, rollers, or any of the hairstyles that can contribute to this condition and further weaken the hair. The main treatment for traction alopecia is to change your hairstyle, have better hair care, avoid any hairstyles that are too tight, and avoid further processing of your hair. If traction alopecia continues, bald spots and hair thinning can develop and be permanent.
In cases of an active infection due to traction alopecia, Dr. Green will prescribe oral antibiotics. Some patients may need oral or topical steroids if the scalp is very irritated or swollen. To re-grow hair, Dr. Green may recommend a combination of PRP, hair vitamins, and topical minoxidil (Rogaine) to maximize hair regrowth.
Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania is a psychiatric disorder in which compulsive hair pulling and twisting can cause bald patches. This hair-pulling disorder is more common in children than adults. It also more commonly affects female patients and is generally related to anxiety. Some patients pull the hair from their heads, while others pull it from the eyebrows or eyelashes. If the hair pulling goes unstopped, the hair loss can be permanent. The best treatment for this disorder is psychotherapy and CBT to deal with the stress affecting you.
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a condition in which stress can cause temporary hair loss due to extreme shock or stress to the body. The hairs are pushed into the resting phase, the telogen phase, for two to four months before the hair falls out. At the same time, the next growth, or anagen phase, does not begin. A few months later, these hairs fall out after the stressful event, and new hair growth is delayed. Clinically, there will not be bald patches, but you will see a general thinning of the hair, which is particularly noticeable after washing your hair. Telogen Effluvium does not lead to complete baldness, but you can lose between 300 to 500 hairs per day, which can cause a profound cosmetically appearing hair loss problem. Although much hair can be shed from Telogen Effluvium, it does not generally result in complete baldness. The hair loss, or Telogen Effluvium, typically begins three months after the precipitating event.
Causes of Telogen Effluvium include serious illnesses, COVID-19, childbirth, extreme dieting or weight loss, anorexia, nutritional deficiencies, withdrawal of hormonal therapy, or surgery. Telogen Effluvium can also occur due to a mineral or vitamin deficiency. Iron deficiency is a common cause of hair loss in women. Medications, such as warfarin, birth control pills, and Accutane (Isotretinoin), can cause this type of hair loss. Telogen Effluvium usually lasts no more than six months and often grows back on its own when the stress is removed. However, in some patients, this type of hair loss can last for a few years without explanation. Besides removing stress, a healthy diet rich in proteins and the amino acid lysine is crucial for proper hair growth. Hair vitamins, containing the B-vitamin, Biotin, are very important in helping to regrow thinning hair.
Anagen Effluvium
Anagen Effluvium is hair loss when you see rapid hair shedding due to medical treatments such as chemotherapy. Chemotherapeutic agents kill cancer cells but stop hair follicle production throughout the body. According to cancer.gov, once chemotherapy is complete, the hair usually grows back on its own. However, the quality of the hair may be affected by chemotherapy.
What types of hair loss are permanent? Scarring or Cicatricial alopecia
Scarring alopecia, also known as cicatricial alopecia, results from the active destruction of the hair follicle, which can cause permanent hair loss and scarring. This type of scarring alopecia, in which the inflammation permanently destroys the hair follicle, is much rarer than non-scarring alopecia. It is important to determine whether the hair loss is nonscarring (non-cicatricial), which is reversible, or scarring, which may be irreversible. Several diseases can cause scarring alopecia. The patches may start small and increase in size over time. Burning, pruritus, erythema, and pain can often accompany hair loss. Dr. Geen does not treat scarring alopecias.
Skin diseases, such as lichen planus, frontal fibrosing alopecia, folliculitis decalvans, or discoid lupus may trigger scarring alopecia.
- Lichen planus is a common skin condition that becomes lichen planopilaris when it spreads to the scalp. In lichen planopilaris, the scalp can become red, irritated, inflamed, and painful. More women than men are affected by this hair loss disease.
- Discoid lupus may also present with scarring alopecia as one of its symptoms. Discoid lupus is a type of cutaneous lupus that can lead to inflammation and scarring on the face and scalp. Treatment consists of treating the underlying skin condition. Treatment may range from topical or oral steroids, intralesional steroid injections, oral medications such as Plaquenil, and topical Minoxidil.
- Folliculitis Decalvans is an inflammatory disease that leads to the permanent destruction of hair follicles and scarring alopecia. Clinically, the scalp is generally inflamed, pruritic, and contains pustules.
- Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is most commonly seen in postmenopausal women. Typically, one sees a receding hairline pattern, which may extend to hair loss in the axillae and eyebrows.
Since scarring alopecia can be progressive, it is vital to diagnose and initiate therapy early to minimize hair loss and formulate a comprehensive treatment plan. Hair may grow back around the scarred area in nearby hair follicles, which can help your cosmetic appearance. Dr. Green will diagnose but does not treat these scarring alopecias.
Hypotrichosis
Hypotrichosis is a rare genetic disorder, an autosomal recessive condition, that affects hair growth. Generally, individuals with this condition have had sparse hair (hypotrichosis) on the scalp since they were infants. The hair is coarse and curled and described as “woolly” hair. Hair is fragile, breaks easily, and cannot grow over a few inches. Over time, the hair loss progresses to complete hair loss on the scalp.
Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair restoration is reserved for patients, both men and women, for whom other, more conservative treatments have failed. Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure where hair follicles are removed from the ‘donor site,’ typically in the back of the scalp, and are transplanted to the balding area of the scalp, known as the ‘recipient site.’ In the past, dermatologists would remove a strip in the posterior scalp, called the follicular unit strip (FUSS), and close the donor site with sutures. The surgeon would then divide that strip into tiny hair follicles and transplant them into the areas of hair loss. A newer method of hair transplant surgery involves having a follicular extraction procedure (FUE), where hair follicles are removed one by one, and the donor area heals with small dots. These single hair follicles are then transplanted into the donor areas of hair loss. Each hair follicle is surgically implanted by creating a tiny hole or slit with a scalpel. The procedure can take 4 to 8 hours, depending on how many grafts are used and the number of assistants helping the surgeon. You will leave with a bandage over your head and need oral antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs for the week following the procedure. Depending on your hair loss, you may require a repeat procedure. New growth takes between 6 and 9 months. Many surgeons prescribe topical minoxidil and PRP injections to maximize the cosmetic results of hair transplant surgery.
Can supplements prevent hair loss?
Vitamin deficiencies can contribute to hair loss, which is why taking some vitamin supplements can help prevent it. Dr. Green recommends supplements that contain B vitamins, Vitamin C, and biotin, which are all useful for strengthening the hair follicle and promoting new hair growth. In particular, Viviscal and Nutrafol are two supplements formulated with vitamins essential for hair growth.
HydraFacial Keravive Scalp Treatment NYC
Dr. Green has been using HydraFacial technology to help rejuvenate the skin. Now, HydraFacial technology has created Keravive, which is a unique office 3-step office procedure to cleanse, stimulate, and hydrate the scalp. Keravive removes impurities and dead skin cells from the hair follicles and replaces vital nutrients, such as antioxidants, peptides, and hyaluronic acid, in the scalp. This 3-step process consists of the following:
- Step 1: Cleanse and Exfoliate, which uses HydraFacial Vortex Technology to remove oils and impurities from the scalp and hair follicles and stimulate circulation.
- Step 2: Stimulate and Nourish the scalp utilizing a unique Peptide Complex Solution. This advanced solution stimulates and nourishes the scalp and hair follicles with proteins and growth factors.
- Step 3: Extend and Enhance the results at home with the HydraFacial Keravive Complex Spray, which nourishes the scalp and hair follicles daily.
HydraFacial Keravive in-office treatment is recommended once a month for three months in conjunction with the Keravive Complex spray for healthier-looking, fuller hair. The treatment’s effects are immediate and long-lasting.

LaserCap for hair loss
The LaserCap is a highly effective prescription-strength laser therapy, which is FDA-approved for hair regrowth in both men and women. It re-energizes inactive hair follicles using Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT), a safe and natural, proven way to increase hair growth. It is particularly effective as a maintenance device for hair growth and is a drug-free alternative for patients who do not want oral medications. The LaserCap is available at the office of Dr. Michele Green and has been proven more effective than other advertised lasers on the market.
Hair Loss Treatments
There are many hair loss treatments by dermatologists today. One of the most popular hair loss treatments currently available at Dr. Michele Green’s NYC office is PRP injections for hair loss:
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) for Hair Loss
Dr. Michele Green was one of the first dermatologists in NYC to treat hair loss with Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) injections. PRP is a holistic, straightforward, and highly effective treatment. After a simple blood draw, your blood is spun in a special PRP separating tube, extracting the platelet-rich plasma. The PRP has all the important growth factors, which are injected into your scalp to re-grow your hair. PRP has been used for years by professional athletes, in conjunction with injections into their joints, to speed up healing naturally. Patients typically benefit from 5 treatments of PRP, spaced one month apart, and annual maintenance treatments to sustain their hair and prevent future hair loss.
PRP Treatment for male and female patients
PRP is a non-invasive injectable treatment for hair loss that uses the patient’s blood. A small blood sample is taken from the patient in a special tube placed in a centrifuge and spun for ten minutes to separate the plasma from red blood cells. The separated plasma contains the PRP (platelet-rich plasma) injected into the scalp to treat hair loss. The plasma that is separated during this process contains growth factors, which are a mixture of proteins and cytokines. The proteins and cytokines are important in stimulating the hair follicles to generate hair growth. The growth factors found in PRP are known to produce the following effects.
- Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) regulates cell growth, stimulating keratinocyte and fibroblast production.
- Transforming Growth Factor (TGF) promotes the growth of new blood vessels.
- Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) stimulates the growth of blood vessels from the existing vasculature.
- Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) promotes granulation during tissue repair.
- Platelet-derived Growth Factor (PDGF) Promotes collagen growth and proteoglycan synthesis, attracting macrophages and fibroblasts to the treated area.
- Interleukins, Macrophages, Keratinocytes, Endothelial Cells, Lymphocytes, Fibroblasts, Osteoblasts, Basophils, and Mast Cells activate fibroblast differentiation and induce collagen and proteoglycan synthesis for healthy cell production and repair of damaged tissues.
- Collagen Stimulating Growth Factor stimulates granulocyte and macrophage proliferation for the growth of healthy tissue and blood cells.
- Keratinocyte Growth factor (KGF) Keratinocyte migration, differentiation, and proliferation may optimize conditions for healing and generation of new skin.
PRP is the only non-invasive procedure available at this time for hair loss. Before PRP, surgical hair transplantation was the only treatment option for those suffering from hair loss. Hair transplantation is an expensive and painful process that removes hair follicles from the back of your scalp and transplants them in areas of the scalp with hair loss. Although today there are several other hair transplantation options, PRP injections are a holistic, non-invasive treatment for hair growth and regrowth.
The ideal PRP candidate is patients experiencing excessive shedding and hair loss without balding – both male and female. And while it can combat early signs of male or female pattern baldness, patients with excessive balding are not the ideal PRP candidates. Patients with hair loss who have intact hair follicles are good candidates for PRP. PRP is safe for most patients, except if you have any blood or platelet disorders, active infections, viral outbreaks (such as shingles), or are on steroids or blood thinners (such as Coumadin). Pregnant patients should also not consider PRP until after they give birth.
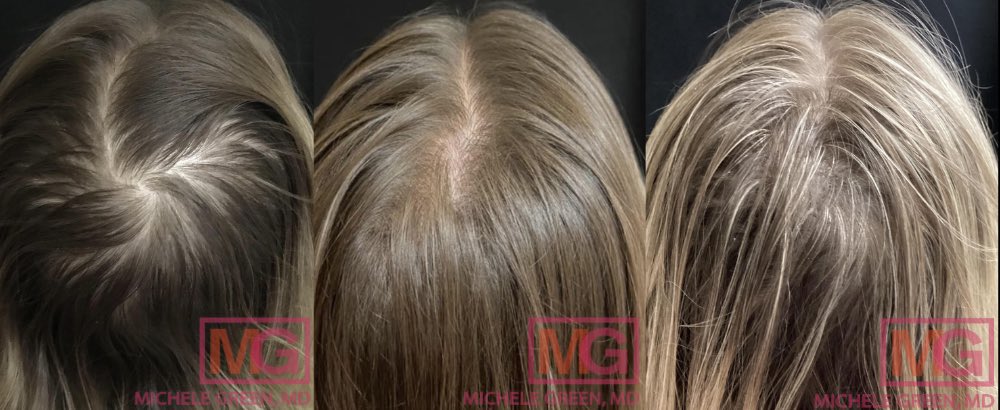

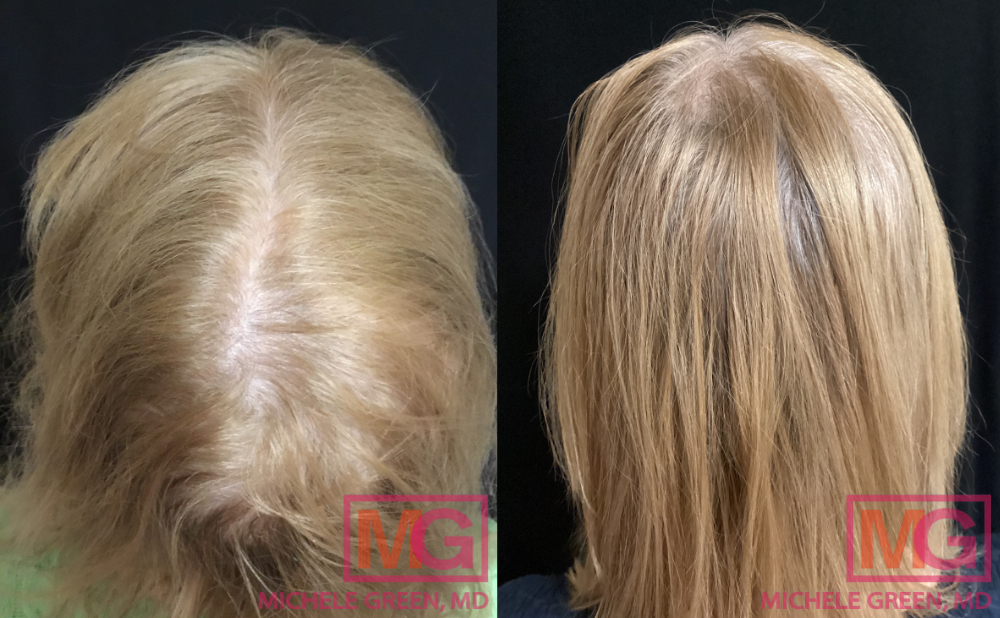
Before and after 3 and 5 sessions of PRP, 6 months and 14 months
PRP Risks and Side Effects
PRP is a safe treatment with no side effects. There is no limit to the number of treatments a person can have. However, depending on the severity of the condition and treatment combination, it can take up to six months to see results. I recommend four consecutive monthly treatments of PRP injections followed by maintenance treatments every four to six months to maintain the best results. The hair growth cycle grows hair at approximately 1.25 cm a month. The results of PRP are continually evaluated, though the results are best judged after six months.
There may be some tenderness on the scalp after injections, and some patients report having a slight headache or pressure in the treated area. You should also limit sun exposure to the treated area for forty-eight hours after the treatment. You can take Tylenol to relieve any discomfort after the treatment. Hair should not be washed for twenty-four hours after treatment. You can resume using hair care products and treatments within twenty-four hours after treatment. No harsh chemicals, hair coloring, or perming should be done within seventy-two hours of PRP hair treatment. You should avoid heavy exercise for twenty-four hours.
Do not use blood-thinning agents such as vitamin E, A, Ginko, Garlic, Flax, Cod Liver Oil, niacin supplements, and essential fatty acids for at least one week after your treatment. Avoid alcohol and smoking for seventy-two hours. Avoid Aspirin, Advil, Motrin, Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Voltaren, and other anti-inflammatory medications for five days after your procedure (if possible).
The results of PRP treatments can be maintained by taking oral prescription medications such as Finasteride (Propecia) or Spironolactone. In addition, taking over-the-counter vitamins such as Viviscal and Nutrafol has been shown to be effective in hair growth. Finally, topical Minoxidil is used daily, and the Laser Cap is used three days a week to promote and maintain hair growth.
Will Creatine cause hair loss?
Creatine is a naturally occurring substance in the body that can also be taken in supplement form. Many athletes take Creatine as a supplement because they believe it improves athletic performance, helps with muscle gain, and speeds up recovery time. However, no conclusive research has demonstrated the effectiveness of the creatine supplement in improving athletic performance and recovery. One study in 2009 found that creatine supplements resulted in higher levels of DHT in the body, which led to the speculation that the supplement caused hair loss. This claim has not been supported by other studies, meaning that there is no conclusive evidence demonstrating that creatine causes hair loss.
Does Creatine promote hair loss?
A study published in 2009 speculated, based on their findings, that creatine supplements caused hair loss. However, this study was flawed due to its small sample size of 20 participants and conclusions that were drawn based on correlation rather than causation. The 2009 study failed to measure levels of free testosterone in the body, and when later studies attempted to replicate the results, researchers found that the ratio of DHT to free testosterone stayed within typical limits, meaning the increased levels of DHT that the 2009 study noted were not clinically relevant. As such, there is no conclusive evidence to support that creatine promotes hair loss.
What types of hair loss does Rogaine help?
Rogaine (topical minoxidil) is the mainstay treatment for patients with androgenetic alopecia. However, it has been an excellent adjuvant off-label treatment for many other hair loss conditions, such as alopecia areata and telogen effluvium. Minoxidil works well both for male pattern baldness and female pattern hair loss. Rogaine is an FDA-approved treatment for hair loss, and both men and women have shown large gains in the number of new hairs grown with daily and continued use.
Can Psoriasis, Seborrheic dermatitis, or dandruff cause hair loss?
Dandruff and seborrhea do not directly cause hair loss. However, the pruritus caused by these conditions leads patients to scratch. This scratching, if severe, can inadvertently injure your hair follicles, leading to areas of hair loss. While dandruff alone will not directly cause permanent hair loss, once these conditions are cleared, any lost hair should re-grow.
How much does hair loss treatment cost in NYC?
The cost of treating hair loss in New York depends on which treatment option you need, the type of healthcare provider from whom you seek treatment, and how many treatment sessions you undergo. Dr. Michele Green will consult with you about your hair loss, take a complete history, and a full examination. Based on the consultation and examination, the best treatment plan for your needs will be created. We will review the prices and procedures with you during your consultation.
Is hair loss normal?
When patients first notice that they’re experiencing hair thinning or hair loss, one of the first questions that many patients have is what is a normal amount of hair loss, if any? It is normal to lose between 50 and 100 strands of hair on a regular day. Sudden hair loss or copious amounts of hair loss may indicate that there is an underlying health condition that is causing the symptoms. Meeting with a board-certified dermatologist, like Dr. Michele Green in NYC,
Is hair loss permanent?
Depending on the type of hair loss, it may be temporary or permanent. The best approach to addressing hair loss and understanding it, whether permanent or temporary, is to schedule a consultation with a board-certified dermatologist, like Dr. Michele Green, in New York City. Dr. Green is an internationally renowned cosmetic dermatologist with over 25 years of experience treating men and women from around the globe for hair loss and hair thinning.
Do Perms cause hair loss?
Unfortunately, depending on the technique used to apply the perm, the process may cause hair to become frail and easily breakable. Weakening the hair shaft by perming could result in hair thinning, although it won’t disturb the hair follicles.
What causes sudden hair loss?
Several types of hair loss conditions can lead to sudden loss of hair, including Alopecia Areata, Telogen Effluvium, and Anlagen Effluvium. Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissue, including the hair follicles. This damage to the hair follicles can lead to bald patches, thinning hair, and slowed hair growth. Alopecia Areata is a genetic condition that can progress to complete hair loss. Telogen Effluvium is another sudden hair loss condition that is caused by a stress-based event, such as severe illness, injury, surgery, or childbirth. The condition causes between 20 and 50% of the hair follicles to enter the resting phase at the same time, leading these hairs to shed at the same time about three months later. Typically, telogen effluvium is an acute condition, and the hair will grow back after six months if the stress is removed. Finally, sudden hair loss can also be caused by Anlagen Effluvium, which is when medical treatment, such as chemotherapy, causes complete or partial loss of hair.
What causes hair loss in women?
There are many potential causes for hair loss in women, ranging from genetic conditions, such as female-pattern hair loss; autoimmune disorders, such as Alopecia Areata; medications, such as birth control pills and antidepressants; and hormone fluctuations associated with puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. Before Dr. Green can generate a treatment plan, it is essential to determine the root cause of the hair loss. As such, at your initial consultation, Dr. Green will examine the treatment area and run blood tests to find the cause of hair loss.
What causes baldness in men?
One of the most common causes of hair loss in men is male-pattern baldness, also known as Androgenetic alopecia. This genetic condition becomes more noticeable with age and affects as many as 50 million men in the United States. Over time, the condition leads to damage to the hair follicles, making them decrease in size and making the growth cycle shorter. Hair loss begins along the temple, eventually moving to the crown of the head. Complete hair loss may be caused by the autoimmune condition called Alopecia Areata, which occurs when the body’s immune system damages hair follicles irreparably.
What causes alopecia hair loss?
Two main types of alopecia can contribute to hair loss: Androgenic Alopecia and Alopecia Areata. Androgenic Alopecia occurs when high levels of free testosterone are converted into DHT, which is an androgen that can bind to hair follicles and damage them. Dr. Green has several treatments available to address Androgenic Alopecia, including platelet-rich plasma injections to improve hair follicle thickness and growth and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors like Finasteride to prevent conversion of free testosterone into DHT. Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes more sudden and unpredictable hair loss. There is a genetic component to the condition, and while the effects can be slowed, they may not be able to be reversed completely.
Which vitamin deficiency causes hair loss?
Certain vitamin deficiencies, including deficiencies in vitamin B, vitamin C, and biotin, can contribute to hair loss or thinning. For patients who are struggling with vitamin deficiencies, Dr. Green recommends supplements such as Viviscal and Nutrafol. These supplements are formulated with essential hair vitamins to strengthen the hair follicle and promote hair growth.
Does wearing a hat cause hair loss?
Traction Alopecia is a type of hair loss that occurs when the hair is pulled consistently by tight hairstyles or headwear. In the affected area, patients may notice broken hair or missing hair, pimples, or sores. Most commonly, Traction Alopecia occurs around the temples, at the front of the hairline, or along the sides of the scalp. Wearing a hat every once in a while does not typically lead to hair loss. However, repeated, daily use of tight or constricting headwear may contribute to thinning or damaged hair.
Does Ozempic cause hair loss?
Ozempic is a medication originally FDA-approved to help with insulin regulation in patients with diabetes. Recently, the FDA approved Ozempic as a weight-loss aid, and it may also be referred to as Wegovy in that context. Hair loss is not a reported side effect of the medication itself. However, hair loss can occur due to sudden weight loss, which occurs while on the medication. Studies found that approximately 3% of patients taking Ozempic as a weight loss aid experienced some form of hair loss.
Does testosterone cause hair loss?
The male androgen DHT is associated with hair loss, as it can bind to hair follicles and damage them. Free testosterone in the body can be converted to DHT (dihydrotestosterone) by 5-alpha-reductase enzymes, leading many to believe that high levels of free testosterone contribute to hair loss. However, there is no direct correlation between high levels of testosterone and hair loss. Rather, there is a genetic component that contributes to whether a patient is pre-disposed to hair loss. Levels of DHT in the body can be lowered with medication like Finasteride, which blocks the conversion of free testosterone into DHT.

How to prevent hair loss and baldness
Many patients wonder “how to prevent hair loss,” and the answer is that the best first step for preventing hair loss and baldness is to schedule a consultation with expert board-certified dermatologist Dr. Michele Green. It is essential to understand the cause of hair loss before developing a treatment plan, as certain hair loss conditions respond to some treatments but not others. When you arrive for your consultation, Dr. Green will examine the treatment area and run blood tests to find the root cause. Once the cause has been determined, Dr. Green will generate a treatment plan that will best meet your needs. Some hair loss conditions cannot be fully stopped or reversed. However, with treatment, hair loss and thinning can be slowed.
How to avoid hair loss
When patients ask “how to avoid hair thinning,” the answer is that several simple lifestyle changes can promote hair health, reduce the symptoms of hair thinning, and prevent hair loss. Stress is one major contributing factor to certain hair loss conditions, and, as such, stress reduction is an important step for avoiding hair loss. Regular exercise can be effective at reducing stress by releasing endorphins. Additionally, good nutrition can help to keep the hair healthy and strong. Extreme dieting can create stress for the body and contribute to hair loss, which is why it is essential to maintain a healthy, balanced diet.
How to stop hair thinning and balding
Suppose you have begun to experience hair thinning and balding. In that case, the best first step is to schedule a consultation with experienced board-certified dermatologist Dr. Michele Green, who will develop a treatment plan that will best meet your needs. Dr. Green will often turn to platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections to strengthen the hair follicle and promote new hair growth. She might pair PRP injections with medication, such as minoxidil, finasteride, or spironolactone, to increase the effects of the treatment. Other in-office treatment options include the Keravive scalp treatment and Laser Cap. No one treatment option is inherently better than another. Rather, it is all about finding the treatment option that will be most effective for you.
How to prevent and treat hair loss today
Hair loss can be stressful and debilitating for men and women alike. The best way to prevent and treat hair loss is to live a healthy lifestyle and to intervene at the earliest indication of hair thinning or hair loss. Eliminating stress, proper nutrition, relaxation, sleep, and hair vitamins all play a part in growing and keeping healthy hair. It is important to avoid hair processing or hairstyles that exacerbate hair loss. Suppose you notice hair thinning or excess shedding. In that case, it is important to consult a board-certified cosmetic dermatologist, like Dr. Michele Green in New York City, as quickly as possible to prevent hair loss from progressing.
Proper identification of the type of hair loss and its cause is the best combination for an effective treatment for hair rejuvenation. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are key to a successful outcome and hair regrowth. Dr. Michele Green is an expert in hair loss in NYC and has helped thousands of men and women with their hair loss problems. If you’re frustrated by thinning hair and hair loss, our practice is here to help. For her dedication to her patients and expertise, Dr. Green is consistently voted one of the best dermatologists in NYC by Castle Connolly, The New York Times, Super Doctors, and New York Magazine. Please contact us online today or call 212-535-3088 to learn more about Dr. Green’s personalized approach to hair loss treatment.
 212-535-3088
212-535-3088