Postpartum Hair Loss
Becoming a new mom brings many changes, with the most exciting being the arrival of your baby. During pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, a woman’s body undergoes numerous changes. In the third trimester, elevated levels of hormones such as estrogen and progesterone influence the hair growth cycle by prolonging the anagen (growing) phase and preventing shedding. This hormonal shift results in fuller, thicker hair. However, after birth, as estrogen and progesterone levels decline, hair in the resting phase begins to shed, which causes postpartum hair loss. Many new moms notice clumps of hair on their pillows in the morning or find their shower drain clogged with strands of hair, which can be upsetting. Fortunately, board-certified dermatologist Dr. Michele Green in NYC specializes in various types of hair loss and can help you manage postpartum hair loss.
Postpartum hair loss is a common condition caused by fluctuating hormone levels during and after pregnancy. It affects between 40% and 50% of all pregnant individuals and, unfortunately, cannot be prevented. However, this condition is temporary and typically lasts from 6 to 15 months after your child’s birth. During this time, Dr. Green offers several lifestyle recommendations to help reduce the appearance of hair thinning and shedding, including specific hair care products and styling tips. For patients looking to thicken existing hair and promote new growth, Dr. Green may recommend in-office treatments, such as platelet-rich plasma injections, to strengthen hair follicles and improve blood flow to the scalp. If you have questions about postpartum hair loss, the best first step is to schedule an initial consultation with experienced New York City dermatologist Dr. Michele Green.
Dr. Michele Green is a globally recognized, board-certified dermatologist with over 25 years of experience diagnosing and treating hair loss, including postpartum hair loss and alopecia areata. Dr. Green adopts a holistic approach to hair regrowth, tailoring each patient’s treatment plan to meet their unique needs and goals. Consistently named one of New York’s top dermatologists by Castle Connolly, New York Magazine, and Super Doctors, she is celebrated for her dedication and expertise. Dr. Green offers a broad array of cosmetic and medical treatments to stimulate hair growth and prevent further loss. Dr. Green was among the first dermatologists in NYC to incorporate Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy into her Upper East Side practice, helping many men and women achieve thicker, fuller, healthier hair that lasts.
What is postpartum hair loss?
Postpartum hair loss is a common condition affecting between 40% and 50% of women who have recently given birth. It is marked by excessive hair shedding in the months after childbirth. Signs include noticing extra hair in the shower drain or on your pillow when you wake up, which can be upsetting. Thinning hair is often most noticeable along the hairline and in those with longer hair. Although the increased shedding can be alarming, true postpartum hair loss is only temporary. How long it takes for hair to grow back and for the hair growth cycle to normalize varies from person to person and depends on the amount of hair shed. This increased hair loss is known as telogen effluvium. It’s hard to predict who will experience postpartum hair loss, as pregnancy effects differ for everyone. Additionally, there is no guaranteed way to prevent or treat postpartum hair loss, but certain lifestyle changes can support hair health and help conceal its effects.
The causes of postpartum hair loss
During pregnancy, estrogen levels increase, which can influence hair growth and shedding. While estrogen levels remain high, your hair stays in the resting phase and does not enter the shedding phase. Therefore, the thick hair often seen during pregnancy is not due to increased hair growth but rather to better hair retention. After childbirth, hormone levels return to pre-pregnancy levels, causing a drop in estrogen. This decrease triggers the shedding phase, which naturally follows the resting phase, leading to more hair loss than usual and excessive shedding. This increased hair loss is known as telogen effluvium.
Hormone levels take time to stabilize after childbirth. Many women notice postpartum hair loss within 3 months of delivery. Hair naturally cycles through growth, resting, and shedding phases. During pregnancy, elevated hormone levels, such as estrogen and progesterone, can delay hair that would normally enter the shedding phase from entering the resting phase. After delivery, as hormone levels decrease, hair that remained in the resting phase during pregnancy enters the shedding phase, leading to increased hair loss. This shedding phase, in which hair falls out, typically occurs between three and five months postpartum. Although timing varies among people, significant hair loss generally begins postpartum.
How to treat postpartum hair loss?
Addressing postpartum hair loss requires special considerations, especially if you are nursing or breastfeeding your newborn. The available medications and treatments for hair loss may differ in safety and effectiveness, and some options might not be suitable for nursing mothers due to potential effects on the baby. It is essential to seek medical advice from a board-certified dermatologist, such as Dr. Michele Green, who will work closely with your board-certified OB-GYN to create a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and to ensure your safety and your baby’s health. This customized approach will consider your individual health situation, the level of hair loss, and your overall postpartum recovery.
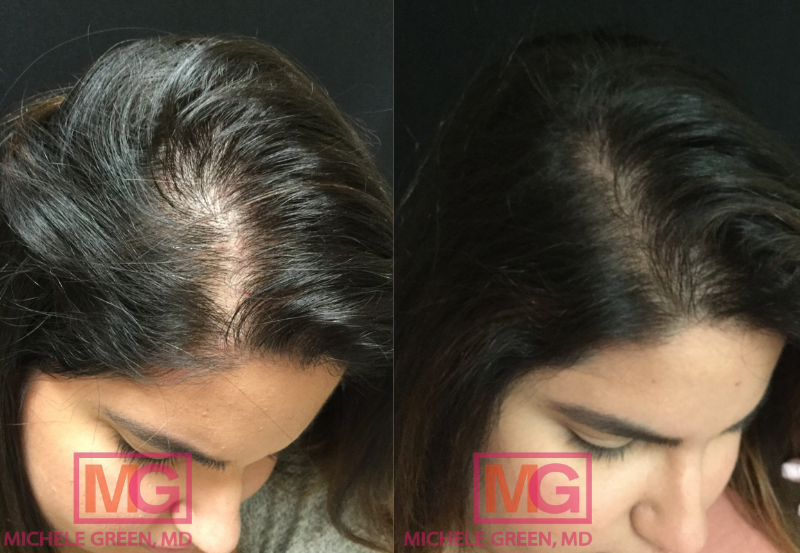
PRP for hair – 2 sessions, 6 months
What to take for postpartum hair loss?
Postpartum hair loss is a common concern for many new mothers, and addressing it effectively requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on nutrition and proper hair care. Key nutrients play a vital role in supporting healthy hair growth. Important vitamins for hair health include iron, zinc, B vitamins, vitamin D, and vitamin C. Continuing to take prenatal vitamins is also encouraged. It is best to take a holistic approach to postpartum hair loss and to recognize that it is typically temporary. One option for supporting hair growth is Nutrafol, a supplement that provides a variety of vitamins and nutrients. Individuals with deficiencies in biotin, iron, vitamin C, vitamin D, or zinc may experience thinning hair or a dull appearance. Nutrafol contains these essential nutrients and can help restore their levels to support optimal hair growth. While Nutrafol can be beneficial for those experiencing hair loss, it’s important to consult your OB-GYN before using any supplements for postpartum hair loss. Prioritizing your baby’s health and wellness means getting your OB-GYN’s approval before starting any new supplements. Additionally, any excessive hair loss or shedding beyond one year postpartum should be discussed with a board-certified dermatologist to rule out other potential causes.
Can you prevent postpartum hair loss?
Postpartum hair loss, or telogen effluvium, is common among many new mothers and is mainly caused by hormonal changes during and after pregnancy. During pregnancy, higher estrogen levels extend the growing phase, making hair look thicker and fuller. After giving birth, estrogen levels drop sharply, prompting hair follicles to move into the shedding phase more quickly than usual. While it may not be entirely possible to prevent postpartum hair loss due to hormonal shifts, it’s important to understand that this condition is usually temporary. Most women notice a gradual decrease in hair shedding within a few months after giving birth, and hair growth typically returns to normal within 6 to 12 months. Maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, and using gentle hair care routines can help support healthier hair during this transitional period.
When does postpartum hair loss stop?
The effects of postpartum hair loss—excessive shedding of hair—stop after the hair follicles that remained in the resting (catagen) phase during pregnancy complete their shedding process. After this phase, hair begins to regrow, though it often does not return to its previous density, and its texture may change. The shedding that was halted in the resting stage during pregnancy generally ends between six and fifteen months after birth. In other words, postpartum hair loss should resolve within this timeframe. If hair loss persists beyond fifteen months, it is advised to see a board-certified dermatologist, as other factors could be contributing to your hair loss.
How long does postpartum hair shedding last?
Postpartum hair loss is a common concern for many new mothers, usually starting around three months after childbirth. This happens as hormone levels, which can fluctuate significantly during and after pregnancy, begin to stabilize. The result is often temporary, excessive hair shedding, known as telogen effluvium, which typically resolves on its own within 6 to 12 months. During this time, many women may notice increased hair shedding, especially when washing or styling. It’s important to realize that this condition is usually temporary and part of the body’s post-pregnancy adjustment. However, if hair loss persists beyond a year or is accompanied by other symptoms—such as persistent fatigue, noticeable bald spots, or changes in scalp or hair texture—it’s best to see a healthcare professional. Consulting a board-certified dermatologist, like Dr. Michele Green, can be very helpful. A detailed scalp and hair exam, along with appropriate blood tests to check hormone levels and nutritional deficiencies, can identify underlying problems. Acting early can be crucial in addressing concerns and considering treatment options, ensuring a healthy recovery for both the hair and the person.
How to prevent postpartum hair loss
Although it may not be entirely preventable, postpartum hair loss can be reduced through certain lifestyle changes. First, choose hair products that won’t weigh the hair down, as this can make thinning hair look worse. Instead, individuals should use volumizing shampoos to boost hair thickness and lightweight conditioners to hydrate without adding extra weight. Additionally, it’s best to avoid hair dryers and tight hairstyles, such as ponytails and braids, which can pull on the hair and increase hair loss. Furthermore, eating a nutritious diet rich in protein, iron, and Vitamin C is key to supporting healthy hair follicles and promoting stronger, thicker new hair growth.
Women who are not breastfeeding can benefit from a hair-loss treatment called platelet-rich plasma (PRP). PRP, or platelet-rich plasma, is an advanced stem cell technology created by drawing the patient’s blood and spinning it in a centrifuge to separate the plasma from red blood cells. The plasma has a platelet concentration three times normal and contains numerous growth factors that stimulate the regenerative cells surrounding hair follicles. The PRP is then injected into different areas of the scalp to encourage hair growth and rejuvenation. While PRP treatment cannot prevent hair shedding, it can accelerate hair growth, helping patients achieve thicker, healthier hair after postpartum hair loss. When you meet with Dr. Green, she will carefully review your medical history and evaluate your hair loss to see if you are a good candidate for PRP injections.
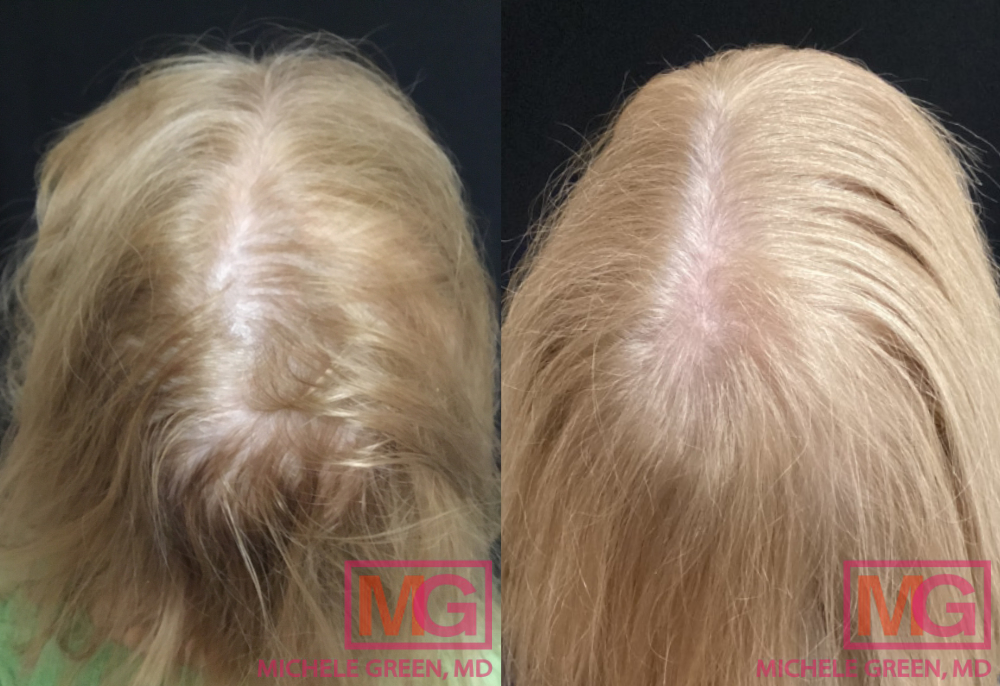
What to do for postpartum hair loss
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, many patients see visible improvements in their hair by their baby’s first birthday. However, there are times when hair regrowth after childbirth does not follow this pattern and occurs more slowly than expected. It is important to continue taking prenatal vitamins, maintain a healthy diet, and check other vitamin and hormone levels to ensure that pregnancy hormones have returned to normal. Dr. Green will conduct a thorough assessment of your hair and scalp, along with your medical history, to rule out systemic conditions, such as lupus or other autoimmune diseases, as the cause of your hair loss.
If you are not breastfeeding, Dr. Green may recommend other treatments for your hair loss, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP), to thicken your existing hair and encourage new hair growth. The procedure involves collecting a blood sample from the patient and spinning it in a centrifuge to separate the red blood cells from the plasma. The plasma contains a highly concentrated volume of platelets packed with growth factors, collagen, and other nutrients. Dr. Green injects the plasma into areas of hair loss to stimulate new hair growth. To determine if PRP injections are the best treatment option for you, schedule an initial consultation with expert dermatologist Dr. Michele Green.
How to combat postpartum hair loss?
To address postpartum hair loss effectively, it is highly recommended to consult a board-certified dermatologist, such as Dr. Michele Green. Working closely with your board-certified obstetrician-gynecologist, Dr. Green can create a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your individual needs, aiming to reduce hair loss and promote healthy regrowth. Postpartum hair loss is common among many new mothers, primarily caused by significant hormonal fluctuations after childbirth. These changes can lead to a condition called telogen effluvium, in which hair follicles enter a resting phase and shed more hair than usual. However, it is important to remember that this condition is usually temporary. As your hormone levels gradually return to pre-pregnancy levels, hair growth typically resumes a normal pattern. In addition to medical consultation, several self-care practices and lifestyle adjustments can support hair health during this transitional period. Proper nutrition, gentle hair care, and stress-reduction techniques can play vital roles in managing hair loss and promoting regrowth.
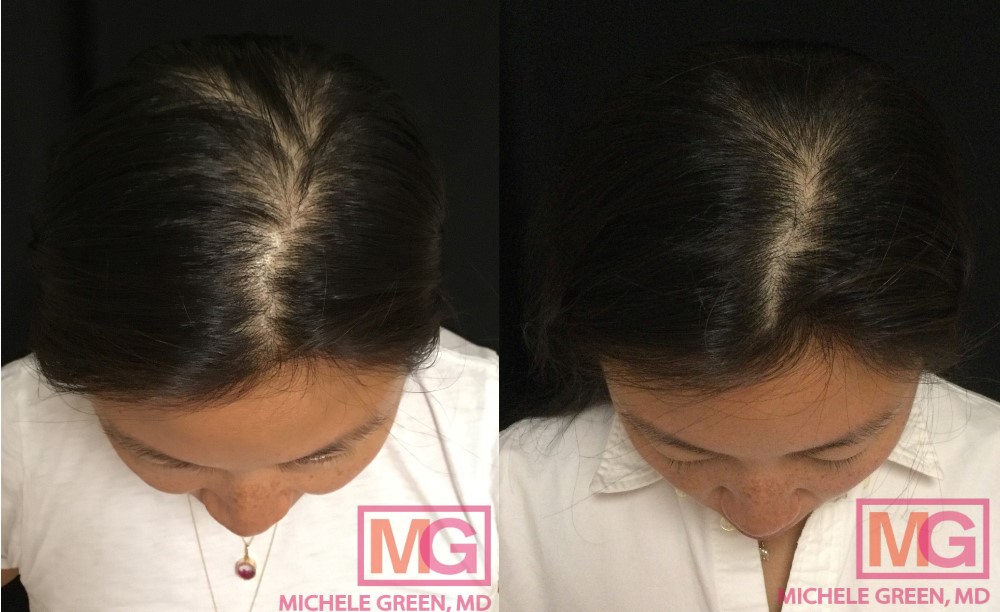
PRP for hair – 3 sessions, 3 months
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why does postpartum hair loss happen?
Postpartum hair loss occurs mainly because of a significant drop in pregnancy hormones, especially estrogen, which can trigger many hair follicles to enter the shedding phase, known as telogen, simultaneously. During pregnancy, elevated hormone levels often prolong the hair growth phase, making hair thicker and fuller. But after delivery, a sudden decline in these hormones can cause an abrupt shift, leading to increased hair shedding. It’s entirely normal to see clumps of hair falling out during activities like showering or brushing. Seeing hair thinning can feel distressing; however, for most women, hair growth will return to normal as hormone levels stabilize. This recovery typically takes about a year, and many notice their hair becoming thicker and healthier over time.
When does postpartum hair loss start?
Postpartum hair loss usually starts around 2 to 4 months after childbirth. This condition, known as telogen effluvium, is mainly caused by hormonal fluctuations, especially a sharp decrease in estrogen after delivery. These hormonal shifts prompt more hair follicles to enter the shedding phase, leading to noticeable hair loss. Shedding often peaks at 4 to 6 months and then gradually lessens. For most women, hair growth rebounds and returns to normal within 6 to 12 months postpartum.
How common is postpartum hair loss?
Postpartum hair loss is a common experience for many women. Hormone levels fluctuate during and after pregnancy, and they decrease postpartum, leading to increased shedding as the body readjusts. About 40-50% of women experience postpartum hair loss due to these hormonal fluctuations.
When does postpartum hair loss peak?
For most women experiencing postpartum hair loss, the peak of excessive hair shedding occurs four to five months after childbirth. Many women notice that their hair is thicker and fuller during the third trimester, when elevated estrogen levels help prevent hair loss. Usually, postpartum hair loss begins 3 to 5 months after delivery. As estrogen levels decrease, the hair in the resting phase during the last trimester re-enters the shedding phase of the hair growth cycle, leading to a notable increase in hair fall at once. This extended shedding phase can last up to 15 months, but most women return to their normal hair growth cycle within a year of giving birth.
How can I stop postpartum hair loss?
Postpartum hair loss happens because of the sudden decrease in levels of the hormones estrogen and progesterone after your baby is born. While high levels of these hormones during the third trimester keep your hair in the resting phase, the rapid drop in estrogen and progesterone causes more hair than usual to enter the shedding phase, resulting in more noticeable hair loss. This can be quite upsetting, but unfortunately, there is no way to prevent postpartum hair loss. The hormonal changes during pregnancy that cause postpartum hair loss are normal and necessary for a healthy pregnancy. Luckily, this condition is only temporary, and your hair growth cycle should return to normal within a year after giving birth.
Does hair grow back after postpartum hair loss?
Yes! Postpartum hair loss is a temporary condition that improves over time. Hair loss occurs during the shedding phase of the hair growth cycle, when new hair grows. As a result, the hair that falls out postpartum will grow back, although it might not have the same thickness as before pregnancy. If alopecia, or excessive hair loss, lasts longer than fifteen months postpartum, it’s best to consult a dermatologist like Dr. Michele Green. Extended hair loss may signal underlying issues, such as thyroid problems, genetic factors, or vitamin deficiencies. For any questions about postpartum hair loss, you can book a consultation with Dr. Green, who can recommend the best ways to encourage new hair growth.
What helps with postpartum hair loss?
Many patients wonder how to reduce the appearance of postpartum hair loss. Although this condition cannot be prevented, several methods can minimize or hide its symptoms. These hair care routines involve simple lifestyle adjustments that can help preserve hair or make hair loss less noticeable.
Hair Care Products: To strengthen your hair, a volumizing shampoo can be helpful. These shampoos often include ingredients like biotin, which coats the hair to reinforce the hair follicle and boost hair fullness. Additionally, products that keep your hair moisturized, such as mousse, can also help create a fuller appearance. It’s best to avoid “conditioning shampoos” or other heavy conditioners, as they can weigh down the hair and speed up hair loss. Instead, choose a conditioner made for fine hair, since these are gentler on the hair follicles and won’t weigh your hair down.
Hair Styling: If you’re dealing with postpartum hair loss, visiting a stylist may be beneficial. This type of hair loss often occurs along the hairline framing the face. Therefore, a middle-parted hairstyle with longer bangs designed to frame the face can make hair loss more noticeable. A haircut with bangs along the forehead and plenty of layers can effectively hide hair loss at the hairline. Additionally, wearing your hair curly might conceal the loss better than straight styles. Stylists also suggest using accessories like headbands or headscarves to cover areas of hair loss.
Does postpartum hair loss happen to everyone?
While postpartum hair loss doesn’t happen to everyone, it’s a common condition—nearly half of all individuals who have given birth experience hair loss after childbirth. Since everyone’s hormonal changes differ, the severity and length of the condition vary from person to person. It can be hard to predict if postpartum hair loss will occur, and some people may find that hair loss happens after one pregnancy but not another.
Can I limit postpartum hair loss?
Unfortunately, postpartum hair loss cannot be prevented. It is a temporary issue caused by hormonal fluctuations that happen during and after pregnancy. There isn’t a surefire way to stop this type of hair loss. However, most women find that their hair returns to its normal state by the time their baby turns 1, with hair shedding and loss improving around 6 months postpartum. You can reduce the severity and promote healthy hair by maintaining a balanced diet and continuing prenatal vitamins. To reduce the risk of hair loss, avoid products that cause hair breakage, especially hot styling tools such as straightening irons, blow dryers, or curlers. Dr. Green also recommends avoiding hairstyles that pull on the scalp, such as tight ponytails and braids. Various hair care strategies can help lessen the effects and visibility of postpartum hair loss, including using volumizing shampoos and light conditioners and trying different hairstyles. Women who are not breastfeeding can encourage hair regrowth and address postpartum hair loss through PRP treatments. Platelet-rich plasma promotes hair regrowth and thickness, helping new mothers achieve thicker, healthier hair quickly.
How to deal with postpartum hair loss
To address postpartum hair loss effectively, it is highly advisable to consult a board-certified dermatologist, like Dr. Michele Green. A qualified specialist can help identify the underlying cause of the hair loss, which may be related to hormonal changes, stress, or other factors associated with the postpartum period. During the visit, Dr. Green will assess the overall condition and appearance of your hair, including thickness, density, and any scalp issues. If needed, Dr. Green will order bloodwork to determine whether there are any underlying causes of the hair loss. This comprehensive evaluation will enable the development of a targeted treatment plan that may include lifestyle adjustments, topical treatments, or other personalized interventions tailored to your specific needs.
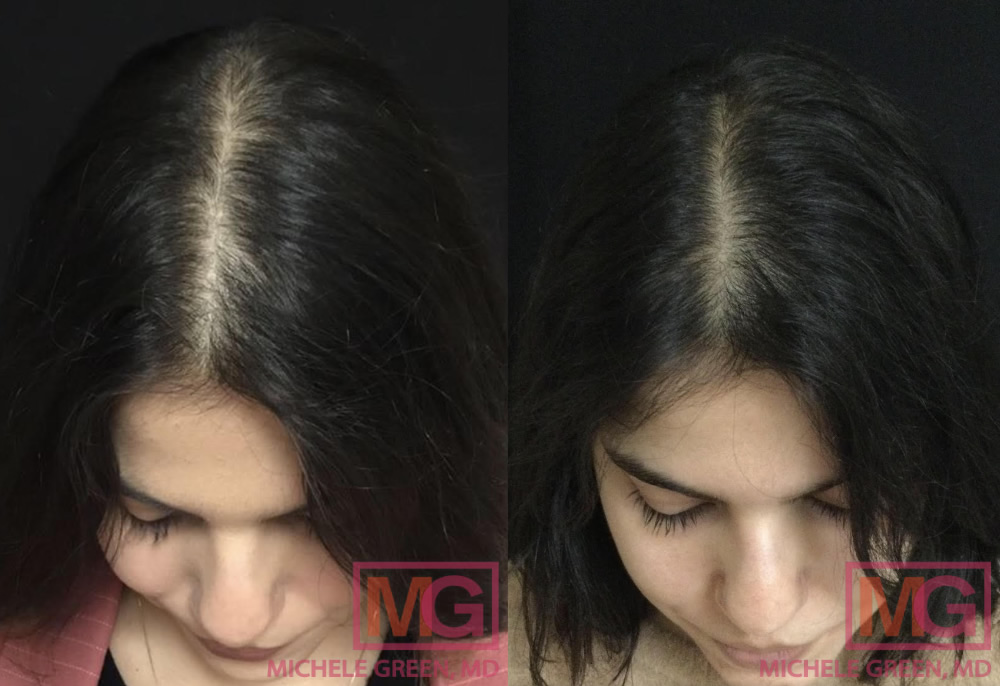
PRP for hair – 4 sessions, 4 months
How do I get started today with treatment for my postpartum hair loss?
During pregnancy, many patients find their hair thicker and fuller than ever before. However, after giving birth, between 40% and 50% of women may experience the concerning condition. During pregnancy, many patients notice their hair becoming thicker and fuller than ever before. However, after giving birth, between 40% and 50% of women may experience postpartum hair loss, a concerning condition. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and postpartum can cause excessive shedding and hair loss in the months following childbirth. Fortunately, postpartum hair loss is usually temporary. For those who continue to experience hair loss, Dr. Green’s private dermatology office offers various treatments to promote thicker, fuller, and healthier hair, including topical Rogaine and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. Patients can also consult Dr. Green for effective hair care options to reduce shedding until the hair growth cycle normalizes, including suitable shampoos and conditioners for daily use.
Dr. Michele Green is an internationally recognized expert in treating hair loss, whether it’s related to postpartum changes or other hormonal or metabolic shifts. Dr. Green specializes in hair-loss treatments, including Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP), and customizes each patient’s treatment plan to meet their specific needs and goals. She is consistently recognized by Castle Connolly, New York Magazine, and Super Doctors as one of New York’s top healthcare providers for her commitment to her patients and expertise. Addressing the early signs of hair thinning is crucial for achieving optimal results. If you are experiencing postpartum hair loss or other types of hair loss, please schedule a consultation with Dr. Michele Green today by calling (212) 535-3088 or contacting her online.
 212-535-3088
212-535-3088