Best Melasma Treatment
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes brown or gray-brown patches darker than the surrounding skin. The most commonly affected areas are the forehead, cheeks, upper lip, nose, and chin. While melasma isn’t harmful, these dark patches can be upsetting, frustrating, and lead to self-consciousness. Fortunately, melasma can be effectively treated and managed with various in-office procedures, prescription creams, targeted skincare products, and lifestyle modifications. When treating melasma, it’s important to consult a board-certified dermatologist, such as Dr. Michele Green in NYC, to ensure effective treatment and achieve a clear, radiant complexion.
Melasma occurs due to excess melanin production in the skin’s melanocytes, which are cells that produce melanin. Although the exact cause of melasma remains unknown, factors such as frequent or prolonged sun exposure, genetics, and hormonal changes have been linked to increased pigment production. Even with daily use of sunscreen, melasma can sometimes seem unavoidable. While it cannot be completely cured, it can be effectively managed with treatments like Cosmelan peels, Mesopeels, microneedling, VBeam laser therapy, topical creams, and targeted skincare. If you’re frustrated by the appearance of melasma or other forms of hyperpigmentation, board-certified cosmetic dermatologist Dr. Michele Green is ready to help.
Dr. Michele Green, based in New York City, is an internationally renowned, board-certified cosmetic dermatologist with over twenty-five years of experience providing some of the world’s most discerning individuals with the best non-invasive treatments, including reducing melasma and hyperpigmentation. She adopts a holistic approach and embraces a less-is-more philosophy in facial rejuvenation, customizing each patient’s treatment plan to their unique skin concerns and overall aesthetic goals. Dr. Green is consistently recognized as one of NYC’s top dermatologists by Castle Connolly, New York Magazine, the New York Times, and Super Doctors for her dedication and expertise. When you consult with Dr. Green at her private dermatology practice in Manhattan’s Upper East Side, she will work with you to develop a personalized melasma treatment plan and provide specific aftercare instructions to keep your complexion clear, bright, and radiant.
What is melasma?
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by blotchy brown, dark brown, or gray-brown patches that are darker than the surrounding skin. It most frequently affects areas of the face, such as the cheeks, nose, chin, upper lip, and forehead. Less often, melasma can also appear on other parts of the body, including the chest, neck, arms, and back. It can be classified as epidermal, dermal, or mixed. In epidermal melasma, the pigment resides in the top layer of the skin, the epidermis. In dermal melasma, the excess pigment is found in the middle layer, the dermis. Mixed melasma, the most common type, involves pigment in both the dermal and epidermal layers. Previously, dermatologists used a Wood’s lamp exam to evaluate the depth of pigmentation. Today, experienced board-certified dermatologists like Dr. Green can assess the treatment area clinically to diagnose and identify the specific type of melasma a patient has.
Melasma is a cosmetic skin condition and is not linked to skin cancer. Its appearance can cause frustration and low self-esteem. Although there is no cure for melasma, a specialist like Dr. Michele Green in NYC can help diminish its look with various skincare products, topical prescriptions, and in-office treatments. After treatment, avoiding sun exposure is especially important because it can trigger melasma to return. If you notice patches of hyperpigmentation that resemble melasma, consulting with Dr. Green in NYC is the best way to develop a personalized plan to reduce their appearance and achieve clear, bright skin.
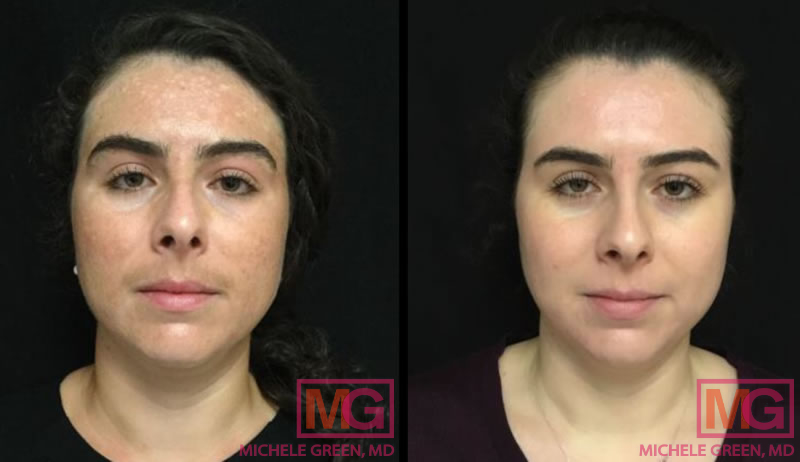

Where does melasma come from?
The precise underlying cause of melasma remains unknown. Melanin, a skin component responsible for pigmentation, is produced by melanocytes, the skin cells that generate melanin. Melasma occurs when melanocytes are overstimulated and produce excess melanin, leading to blotchy, discolored patches of skin that are darker than the surrounding area. Although a specific, identifiable cause of melasma has not yet been determined, certain factors can trigger or worsen it, including:
- Sun exposure — The most common trigger for melasma is direct sunlight. Ultraviolet light, UVA, and UVB rays stimulate melanocytes to produce more melanin. Even minimal sun exposure can trigger a recurrence of melasma, even after treatment. Protecting your skin from UV rays is vital to prevent melasma from returning post-treatment.
- Tanning beds — Like direct sunlight, tanning beds emit harmful UV rays and visible light that can worsen skin pigmentation and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Hormone fluctuations — Changes in hormones, particularly rising levels of estrogen and progesterone, have been linked to melasma development. Pregnancy, birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, and hormone replacement therapy can all trigger melasma since they influence estrogen and progesterone levels. Melasma is often called chloasma or the “mask of pregnancy” because it frequently appears on the faces of pregnant women.
- Genetics — Between one-third and one-half of people with melasma have a family history of the condition. Identical twins often share symptoms, and those with close relatives affected by melasma are more likely to develop it themselves.
- Skin Tone — Melasma is more common among individuals with light to medium brown skin tones (Fitzpatrick skin types III and IV) and darker skin tones (types V and VI) than in those with fairer skin. People with darker skin are more susceptible because their skin contains a higher density of melanocytes, which enables them to produce more melanin.
- Oral Medications — Certain oral antibiotics, cardiac drugs, and other photosensitizing medications can trigger or worsen melasma. These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antipsychotics, and antiseizure medications.
- Thyroid Disease — Currently, it is believed that thyroid disease may contribute to melasma in some patients, as many individuals with melasma also have thyroid conditions. Studies have shown elevated serum TSH, anti-thyroid peroxidase, and anti-thyroglobulin antibodies in patients with melasma. In fact, the occurrence of thyroid disease is four times higher in patients with melasma compared to the general population.
- Stress — While research is ongoing, the stress hormone cortisol is believed to be associated with the development of melasma. Long-term stress can increase hormones involved in melanin (pigment) production. More research is needed to find the exact cause of melasma. Other factors, like pregnancy, thyroid disease, UV exposure, and certain medications, are more likely to trigger melasma.
Which facial areas does melasma appear in?
The most common areas of the face affected by melasma are the upper lip, cheeks, bridge of the nose, and forehead. Although melasma mainly affects the face, it can also develop on the forearms or neck in some individuals. Since sun exposure is a major factor in the development of melasma, it can appear on any part of the body that gets significant sunlight. Because of this, melasma may look darker during the hot summer months when the skin is exposed to more UV light, and it often fades somewhat in the winter.
What is a melasma mustache?
The term “melasma mustache” refers specifically to hyperpigmentation of the upper lip. The same underlying factors that contribute to melasma on the rest of the face are responsible for the development of melasma on the upper lip. UV exposure, in combination with hormonal and genetic factors, triggers the activation of melanocytes in the skin. The melanocytes become hyperactive and produce an excess of melanin, the component in the skin that is responsible for pigment. In the case of the “melasma mustache,” the hyperpigmentation is exacerbated on the upper lip.
Is melasma the same as dark spots?
No, not all dark spots on the skin are melasma. Melasma is a specific type of hyperpigmentation that appears as dark brown or gray patches. Although the exact cause of melasma is unknown, certain risk factors can make it worse, such as sun exposure, tanning beds, hormonal changes (like pregnancy and using birth control), specific medications, skin tone, genetics, and thyroid disease. There is no cure for melasma, and the discoloration can return even after treatment if proper sun protection isn’t used.
Dark spots are pigmented areas on the skin that are darker than the surrounding skin tone. Sun spots and freckles are caused by excess melanin production due to prolonged sun exposure. These spots show up as small, darker patches on the skin. They can be effectively treated with various non-invasive cosmetic procedures. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) refers to dark spots that develop after skin inflammation, such as from acne, injuries, eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis, or improper laser treatments. PIH may fade on its own over time or be treated with in-office procedures and topical skincare.
It’s important to tell the difference between dark spots, hyperpigmentation, and melasma, since the treatments vary widely. Most lasers used to remove sun spots and freckles should not be used for melasma and could make it worse. An experienced, board-certified dermatologist like Dr. Green understands how to tell the difference and can create a treatment plan that leads to clear, radiant skin.
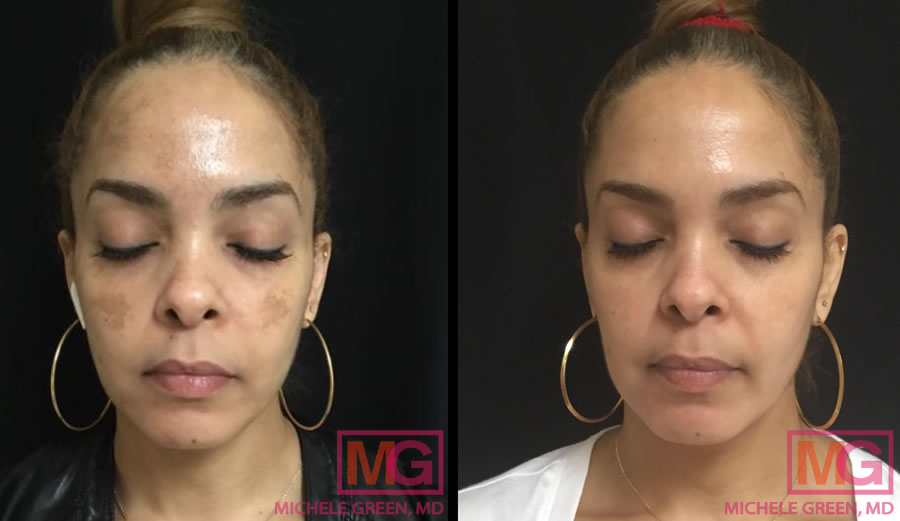

Cosmelan: 10 weeks before & after
Will melasma go away on its own?
Patients often ask, “Will my melasma ever go away?” The answer depends on the individual, primarily based on what initially caused the melasma. For those who develop melasma during pregnancy or due to taking oral birth control pills or other hormone-changing treatments, it may naturally fade after pregnancy or once the hormonal medications are discontinued. However, for many individuals, melasma is a skin condition that requires cosmetic treatments to improve the appearance of hyperpigmented patches. Melasma treatment is an investment, and since it cannot be permanently cured with skincare alone or in-office procedures, prevention remains the best way to keep it under control. When working with Dr. Green to treat your melasma, she will provide all necessary aftercare instructions to help you achieve and maintain a clear, healthy, and radiant complexion.
Can melasma be treated?
Melasma is a notoriously difficult skin condition to treat, as many common treatments for dark spots, such as laser procedures, can actually worsen the symptoms. Since melasma can be very challenging to manage, prevention is one of the most effective strategies. Preventive measures usually include limiting sun exposure and discontinuing any medications or skincare products that may contribute to its development. These methods can help prevent melasma, dark spots, and other forms of hyperpigmentation. Dr. Green consistently recommends applying a daily broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 50 or higher. The best way to prevent unwanted pigmentation, signs of premature aging, and reduce the risk of skin cancer is to protect the skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays.
When unwanted melasma or hyperpigmentation appears on the skin, it can be effectively treated with targeted in-office procedures and specialized topical creams. According to melasma researcher AJ Pandya, the most effective treatment method is a combination of various topical and in-office therapies. The best way to determine which combination is right for you is to schedule a consultation with a board-certified dermatologist, Dr. Michele Green. She will evaluate your melasma and skin to identify the most suitable treatment options based on your skin type, skin tone, and the specific type of melasma you have.
Best Dermatology Treatment Options for Melasma
Chemical peels for melasma
A chemical peel is a skin resurfacing procedure that can improve skin tone and texture. During a chemical peel, Dr. Green applies a chemical solution to the skin’s surface to gently and effectively remove discolored, dead skin from the outer layers of the epidermis. This chemical exfoliation encourages skin cell turnover, leading to unclogged pores and the correction of uneven skin tone, revealing a vibrant, healthy glow. Dr. Green can tailor each chemical peel to meet her patients’ specific needs and goals. Depending on the strength and type of peel used, it can enhance skin texture, reduce the appearance of acne breakouts or scars, and diminish sun damage, fine lines, wrinkles, and melasma. For patients with sun damage and pigment irregularities like hyperpigmentation or melasma, Dr. Green often recommends a trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peel. However, TCA peels are not suitable for every skin type or tone, and it is essential to consult with an expert, such as a board-certified dermatologist, to ensure the peel is safe and effective for you.
Cosmelan peel to remove melasma
The Cosmelan peel is a two-step professional treatment used to target melasma and other forms of hyperpigmentation. In the first step, Dr. Green applies the Cosmelan 1 mask to the affected areas. The mask stays on for several hours, with the exact time determined by Dr. Green based on the severity of the pigmentation, skin tone, and skin type. The mask can be easily removed at home by the patient using a gentle facial cleanser. The second step involves applying specific topical products from the Cosmelan line, including a proprietary Cosmelan 2 depigmentation cream, a gentle moisturizer, and a tinted sunscreen. These products are used after the treatment to help maintain the results and keep the skin free of excess pigment. The patient returns four weeks after the initial treatment for a re-evaluation and potentially a touch-up with Cosmelan if any hyperpigmentation remains.
Cosmelan causes an initial “peeling” effect, leaving the skin smooth and significantly reducing the appearance of facial hyperpigmentation. Dr. Green prefers Cosmelan because it is a simple, safe treatment with minimal downtime that delivers impressive results, helping patients look and feel their best. Cosmelan is safe and effective for all skin tones, including those with darker skin, which may not be suitable candidates for other chemical peels.
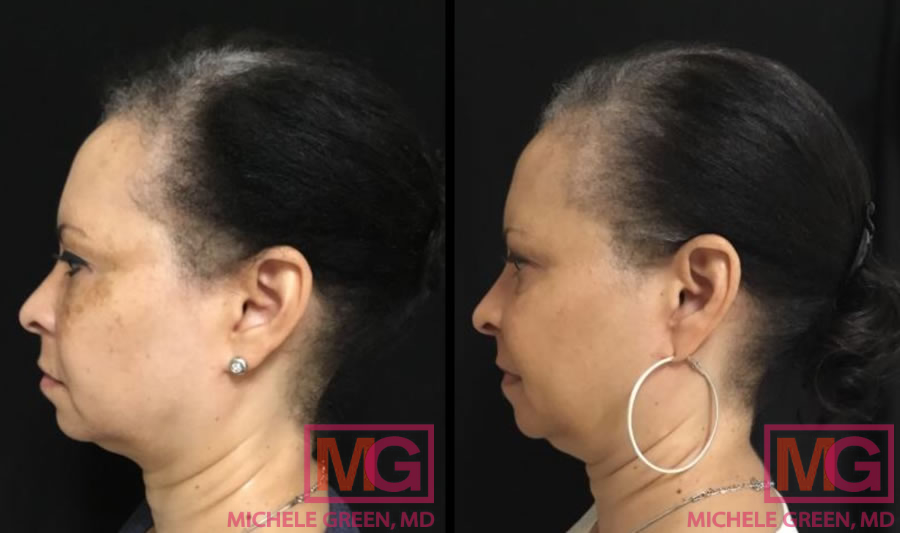
Cosmelan 11 months before and after
Mesopeels for Melasma
A Mesopeel is a specially formulated chemical peel designed to reduce and eliminate hyperpigmentation, including melasma, from the skin with minimal recovery time. Mesopeels use active skin-lightening ingredients like tranexamic acid, kojic acid, and azelaic acid to lower melanin levels, inhibit melanin production, and brighten the skin. They are very gentle and can be performed on patients of all skin types and tones. Additionally, they can be applied to the face and other areas of the body, such as the neck, chest, back, buttocks, and inner thighs. Patients typically need six treatment sessions to achieve optimal cosmetic results, while those with more severe melasma may require additional sessions.
Microneedling with depigmentation serum
Microneedling, also known as collagen induction therapy, is a safe and effective treatment for enhancing skin tone and texture. It can also help diminish the appearance of melasma, especially when combined with a specially formulated depigmenting serum. This minimally invasive cosmetic procedure involves a practitioner using a handheld device with tiny, sterile microneedles to create controlled trauma on the skin’s surface. The procedure stimulates the skin’s natural healing process and accelerates skin cell turnover, resulting in a smoother texture and a brighter, more even tone. One advantage of microneedling is that it creates microchannels that boost the skin’s ability to absorb topical solutions. For melasma, Dr. Green applies a proprietary depigmentation serum rich in skin-lightening and brightening ingredients to reduce hyperpigmentation and clear the skin. Most patients typically need a short series of 3-6 sessions, spaced approximately one month apart, to achieve optimal skin rejuvenation results. Patients appreciate the minimal downtime and mild side effects, which usually include redness and swelling in the treated area.
VBeam laser to treat melasma
The VBeam laser is a pulsed dye laser designed to target red pigmentation on the skin, including facial redness, rosacea, broken capillaries, spider veins, red acne scars, and red stretch marks. It is also highly effective in reducing redness and inflammation associated with melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. This laser works by emitting a 595nm wavelength to eliminate red pigments in the skin. During treatment, the surrounding skin remains unaffected, resulting in no downtime. Typically, 4 to 6 laser sessions, spaced one month apart, are recommended for optimal results.
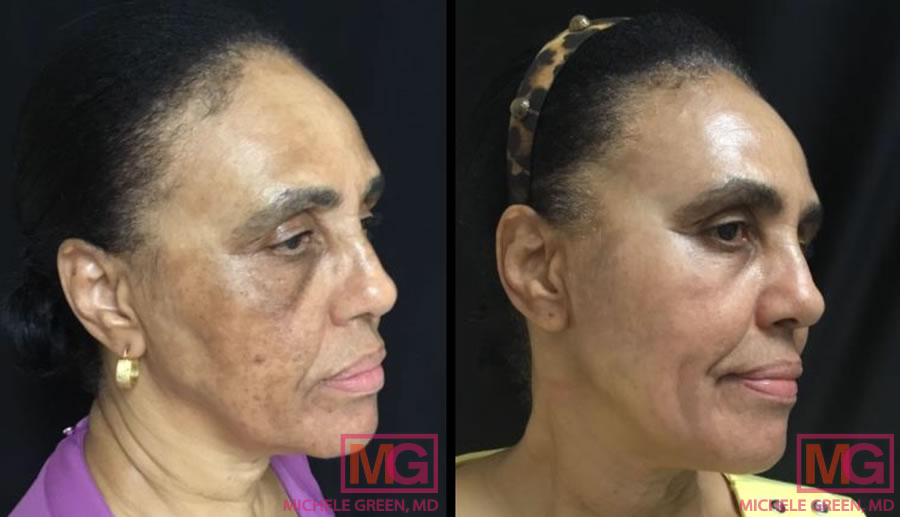
Cosmelan 8 months before and after
Which oral medications can help treat melasma?
Treating melasma can be a lengthy process, and relying solely on topical treatments may not be suitable for everyone. For those struggling to manage melasma with topicals alone, an oral medication called tranexamic acid can be added as a supplement. Tranexamic acid is commonly used topically for melasma and taken orally by women with heavy or painful periods. Current research indicates that off-label oral tranexamic acid might be effective in treating melasma by blocking melanocyte activity, reducing excess melanin production, and preventing melanin transfer to skin cells. When combined with topical treatments, oral tranexamic acid may help diminish the appearance of melasma and promote a clearer, more uniform skin tone. If you’re interested in whether oral tranexamic acid is suitable for your melasma, schedule a consultation with board-certified cosmetic dermatologist Dr. Michele Green.
Can laser treatments remove melasma?
When researching effective treatments for melasma, many patients wonder, “Which laser treatment is best for melasma?” Unfortunately, no lasers should be used to treat melasma. While Fraxel and IPL lasers can reduce sun spots, age spots, and other forms of hyperpigmentation, they may actually deepen the pigmentation of melasma into the skin. Unwanted side effects from inappropriate laser treatments for melasma include increased hyperpigmentation, burns, and scarring. Once laser treatment has been used, melasma can become even more difficult to remove. Dr. Green treats melasma with Cosmelan peels, Mesopeels, chemical peels, VBeam laser treatment, and microneedling to prevent worsening of existing hyperpigmentation. Treating melasma is challenging, and no single treatment works best for every patient or skin type. During your initial consultation, Dr. Green will examine the treatment area and develop a personalized plan that is both safe and effective for your specific skin type.
What is the best cream for melasma treatment?
A proper skincare routine is vital for patients with melasma to improve treatment outcomes. Topical skincare products are also essential to prevent melasma from returning after treatment. Dr. Green developed a proprietary skincare line, MGSKINLABs Inc., with specially formulated products to address various skin concerns, including melasma. When you consult with Dr. Green, she will design a personalized skincare routine that combines prescription and topical treatments to reduce dark patches and help achieve a clear, radiant, and lasting complexion.
Hydroquinone is an ingredient found in prescription skin-bleaching creams that helps lighten hyperpigmentation and melasma. Its skin-brightening effects result from disrupting melanocytes, the skin cells responsible for producing melanin, or pigment. Hydroquinone should not be used long-term and must only be applied under the supervision of a board-certified dermatologist like Dr. Green. Overuse or improper use of hydroquinone can cause skin irritation and worsen melasma. Additionally, hydroquinone increases the skin’s sensitivity to sunlight, so diligent sun protection is crucial while using the topical.
Retinol and retinoids can be effective skincare ingredients for patients with melasma. These vitamin A derivatives work by increasing skin cell turnover, stimulating collagen production, and exfoliating dead, discolored skin cells to reveal healthier, new skin. With consistent use over time, noticeable improvements in skin tone and texture can be seen. Tretinoin is a high-strength vitamin A derivative that is not available over the counter and must be prescribed by a healthcare professional. Retinols are available over-the-counter and tend to be less irritating than prescription-strength retinoids. The Essential Antioxidant Infusion from MGSKINLABs features a unique blend of vitamin A and other nourishing vitamins and minerals to rejuvenate the skin and reduce pigmentation. Patients with sensitive skin may find retinol or tretinoin irritating, potentially causing redness, flaking, stinging, dermatitis, or worsening hyperpigmentation. These patients can use a short course of topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and prevent melasma from worsening.
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant with many renewal properties, making it a valuable addition to any melasma skincare routine. Besides enhancing overall skin tone and texture by promoting collagen production and skin cell growth, vitamin C also inhibits melanin synthesis by blocking the enzyme tyrosinase. Dr. Green’s MGSKINLABs Vitamin C formulation, the Vita-C Serum, contains a high concentration of vitamin C and is designed to promote skin cell renewal and collagen synthesis, leading to a reduction in hyperpigmentation and a clearer, healthier complexion.
Other effective skin lightening agents include kojic acid, azelaic acid, and tranexamic acid, which work by decreasing tyrosinase activity and inhibiting melanin production. The Skin Brightening Cream from MGSKINLABs features a unique blend of kojic acid and fruit extracts to reduce hyperpigmentation and promote a more even skin tone.
What is the best sun protection for melasma?
While in-office treatments and topical skincare products can help treat and manage melasma, nothing is more effective for melasma care than sun protection. Patients with melasma should avoid sun exposure, as UV rays can trigger or worsen melasma and cause recurrence after treatment. Many melasma treatments also increase skin photosensitivity, and UV exposure during this time can exacerbate existing melasma. Therefore, patients must always wear a broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays, which can stimulate melanocytes to produce melanin. Dr. Green’s own Hydrating SPF 50, from her MGSKINLABs Inc. line, offers broad-spectrum coverage with a smooth, silky finish to ensure sun protection and comfort. Sunscreen should be worn daily, as UV rays can penetrate clouds and windows and reflect off puddles and snow.
For optimal protection, Dr. Green suggests applying both a chemical and a physical sunscreen to your skin. Chemical sunscreens work by absorbing heat energy from the sun’s rays and reacting chemically within the skin. Physical sunscreens usually contain ingredients such as zinc oxide, iron oxide, or titanium dioxide, and they work by sitting on the skin’s surface to create a barrier against strong UV rays. By layering two sunscreens, you can better protect your skin from the sun and help prevent the development or worsening of melasma. Wearing a wide-brimmed hat, large sunglasses, and sun-protective clothing is also an effective way to boost your sun protection and prevent melasma from worsening or returning.
Is melasma permanent?
The severity and longevity of melasma differ from person to person. Patients who develop melasma during pregnancy or because of birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, or hormone replacement therapy may see their skin return to normal after giving birth or stopping hormone medications. However, for most people with melasma, the dark patches will not disappear without some form of cosmetic treatment. Additionally, melasma can become harder to treat after laser procedures such as Fraxel, IPL, and Picosure, as these can cause pigment to settle deeper in the skin. If you notice brown or gray patches on your face, it is important to consult with a specialist, such as board-certified dermatologist Dr. Michele Green in New York City. She can help you develop a personalized treatment plan to address and manage melasma, helping you achieve clear, radiant, and evenly toned skin that lasts.
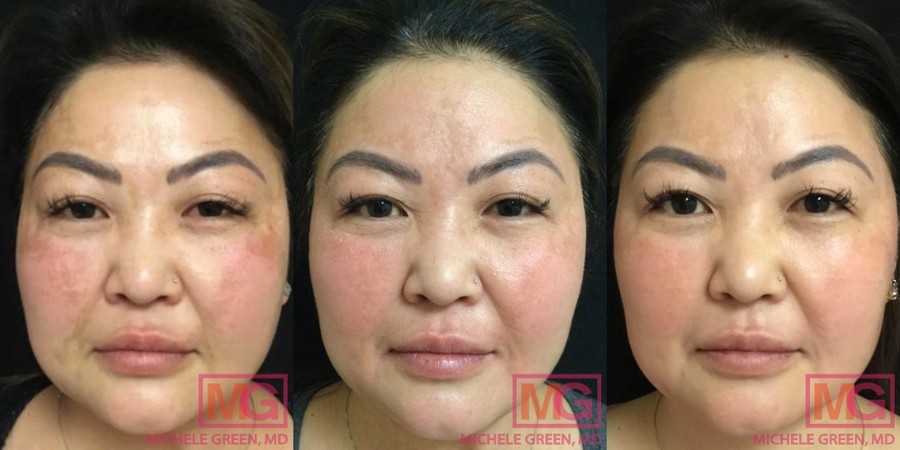
Cosmelan 6 weeks before and after
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Melasma:
Is melasma hyperpigmentation?
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation characterized by patches of brown or grey-brown skin discoloration. Hyperpigmentation is a broad term for areas of skin that are darker than your natural skin tone. In addition to melasma, common types include sun spots, freckles, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Different types of hyperpigmentation may require specific treatments to effectively reduce them, which is why patients should consult an experienced, board-certified dermatologist for a safe and effective cosmetic treatment plan. Dr. Green in NYC is a board-certified dermatologist with over 25 years of experience providing some of the world’s most discerning clients with top non-invasive treatments for hyperpigmentation and melasma. When you meet with Dr. Green, she will collaborate with you to create a personalized treatment plan tailored to your unique skin type, concerns, skin tone, and aesthetic goals.
Where can you get melasma?
Melasma patches typically appear on the forehead, upper lip, and cheeks, but they can also affect the chin, nose, neck, back, and arms.
Who gets melasma?
Certain groups of people are more prone to melasma than others. Most individuals with melasma are women. While men can develop melasma, according to the American Academy of Dermatology, only 10% of people with melasma are men. Melasma is more common in those with light to medium brown skin tones (Fitzpatrick skin types III and IV) and darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick skin types V and VI) than in those with fairer skin. Patients with darker skin are more susceptible because they have a higher density of melanocytes in their skin, which allows for greater melanin production compared to those with lighter skin. Additionally, people with a family history of melasma or facial hyperpigmentation are more likely to develop it.
Is melasma dangerous?
No, melasma is not dangerous. It is not a sign of skin cancer, and it does not have the potential to develop into skin cancer or any other harmful skin condition. However, some skin cancers may resemble melasma in certain ways. If you are worried about a brown or dark lesion on your skin and are unsure whether it is a sign of skin cancer or melasma, schedule an appointment with a board-certified dermatologist, such as Dr. Green. During your appointment, Dr. Green will thoroughly review your medical and family history and then clinically evaluate the hyperpigmented areas to rule out any serious skin conditions. A skin biopsy may be performed and sent to the lab for further examination as part of a routine check to rule out melanoma and other types of skin cancer, if necessary.
When does melasma start?
There is no clear understanding of when melasma will first appear on the skin. Some people experience melasma in their youth, while others may only develop it after excessive sun exposure, pregnancy, or taking medications containing estrogen or progesterone. Generally, melasma results from an increase in melanin, produced by overactive melanocytes in the skin. It is not known why these melanocytes are stimulated to produce excess melanin, leading to areas of concentrated pigment. However, certain risk factors are known to worsen melasma, including sun exposure and hormonal fluctuations.
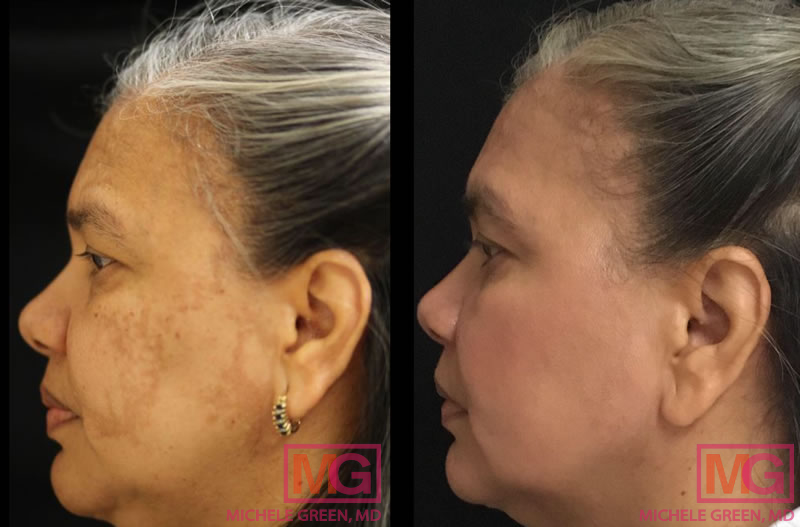
Cosmelan 1 year before and after
How to improve melasma dark spots
The first step in treating melasma and dark spots is to schedule an appointment with a board-certified dermatologist, such as Dr. Michele Green. Dr. Green provides a variety of non-invasive treatments for melasma, including the Cosmelan peel, which has proven to be highly effective in treating stubborn melasma and hyperpigmentation. She may also recommend using Mesopeels, microneedling, or a VBeam laser to reduce dark spots further. Additionally, using skin-lightening products, with or without hydroquinone, and light chemical peels can speed up and improve the treatment of melasma. After examining the area, Dr. Green will suggest a customized series of treatments tailored to your needs.
What makes melasma worse?
Patients often ask, “Why is my melasma worsening?” Melasma occurs when skin cells called melanocytes are triggered to produce excess pigment, resulting in dark patches on the skin. Melanocytes are sensitive to UV exposure and can remember past exposures. Sun exposure, tanning beds, and other sources of UV light often stimulate melanocytes to produce melanin. Therefore, individuals should practice proper sun protection, including applying suitable sunscreen, to help treat melasma. Otherwise, the dark patches may return even after successful treatment. Hormonal changes also contribute to melasma, and conditions that cause hormone fluctuations—such as pregnancy, thyroid issues, or use of certain medications or oral contraceptives—may trigger its development. When you consult with Dr. Green at her private dermatology office in Manhattan’s Upper East Side, she will recommend the best treatments for resolving your melasma and advise on proper aftercare to maintain optimal results and prevent future flare-ups.
Why is melasma difficult to treat?
Various risk factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, thyroid disease, and family history, can trigger melasma. It occurs when melanocytes in the body overproduce melanin. With many triggers that can exacerbate the condition, treating melasma is a complex process. Some treatment options that work for other types of hyperpigmentation, such as laser treatment, can actually make melasma worse. That’s why the best first step is to schedule an appointment with a board-certified dermatologist, like Dr. Michele Green in New York.
Does melasma ever go away?
Depending on the cause of melasma, it can sometimes fade on its own. Melasma is a complex skin condition influenced by various factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and sun exposure. Melasma caused by birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, hormone replacement therapy, or pregnancy may resolve naturally once these hormone treatments are stopped or after pregnancy ends. Unfortunately, for most people, melasma is a long-term condition that often requires cosmetic treatments to improve. Additionally, melasma can return even after effective treatment, which is why avoiding the sun and using targeted skincare products after treatment are crucial to prevent recurrence. An experienced, board-certified dermatologist like Dr. Green in NYC can help you develop a personalized melasma treatment plan to eliminate it for good and achieve clear, radiant skin.
Will melasma go away after pregnancy?
It is very common for pregnant women to develop what is often called chloasma or “the mask of pregnancy.” In pregnant women, melasma typically appears on the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and chin, giving the face a mask-like appearance. Hormonal changes during pregnancy, especially the rise in female hormones like estrogen and progesterone, cause this type of melasma. The best way to manage facial hyperpigmentation or melasma during pregnancy is to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 50 and limit sun exposure, as many standard melasma treatments are not recommended during pregnancy. Usually, melasma that occurs during pregnancy tends to resolve on its own sometime after childbirth, as hormone levels return to normal. Patients who still see melasma after pregnancy can consult a board-certified dermatologist, Dr. Green, for safe and effective treatment. Dr. Green is a dermatologist with over 25 years of experience providing medical advice and treating patients from around the world. In her private New York City dermatology office, she uses her expertise to create personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient, ready to address the melasma caused by your pregnancy.
What is the best melasma treatment?
Patients often ask, “What is the most effective treatment for melasma?” The best way to treat melasma is to start by consulting an experienced, board-certified dermatologist like Dr. Michele Green in NYC. Melasma is a complex skin condition, and many traditional treatments for other types of hyperpigmentation, such as certain laser procedures, can worsen its appearance or make it more difficult to treat. Some of the most effective in-office options for melasma include chemical peels, Cosmelan peels, Mesopeels, microneedling with depigmenting serum, and VBeam laser treatments. Skin-lightening topical treatments and skincare products may also be recommended, especially those containing active ingredients like vitamin C, hydroquinone, azelaic acid, kojic acid, or tretinoin. Typically, patients achieve the best skin rejuvenation results when a personalized combination of topical therapies and in-office treatments is used. Dr. Green will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific concerns and aesthetic goals, helping you look and feel like the best version of yourself.
What treatments should be avoided with melasma?
Many lasers suitable for hyperpigmentation treatment should be avoided when dealing with melasma. Laser procedures like Fraxel or IPL are great for sun spots and age spots; however, these lasers can drive melasma pigmentation deeper into the skin, worsening its appearance and complicating treatment later. While some lasers claim to effectively treat melasma, it is usually best to rely on proven methods like chemical peels or microneedling that are safe and effective for this condition.
What is the best treatment for melasma at home?
The most effective way to treat melasma at home is by limiting sun exposure and following a targeted skincare routine. Sun exposure is the main trigger for worsening melasma symptoms since UV rays boost melanin production in the skin. Using a broad-spectrum SPF 50 and wearing sun-protective clothing, like a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses, can help reduce melasma dark spots and lower the chance of it coming back after treatment. A proper skincare routine for melasma includes products with active skin-lightening ingredients such as vitamin C, tranexamic acid, kojic acid, azelaic acid, niacinamide, and glycolic acid. Prescription hydroquinone or retinoids can also be used at home to lighten pigmentation even more and achieve a more even skin tone.
How long does it take for melasma to go away?
The time it takes for melasma to fade varies based on several factors, including the type of treatment used and the triggers that cause flare-ups. Patients experiencing melasma flare-ups due to hormone changes from pregnancy or oral contraceptives may notice that the melasma fades without medical treatment after pregnancy or switching birth control methods. While some patients may see improvement with treatments within a few weeks, melasma usually improves gradually over time. It can take many months to see a lightening of hyperpigmentation, especially if it was initially treated with lasers improperly. When you see Dr. Green, she will create a personalized combination of in-office cosmetic procedures and customized skincare products designed to reduce your melasma.
Does insurance cover melasma treatment?
Most insurance companies do not cover melasma treatment because it is considered cosmetic. However, it is always best to contact your insurance provider directly to confirm your coverage.
Can you cure melasma?
Although there is no cure for melasma, its appearance can be managed and treated with various in-office procedures, prescription creams, and targeted skincare products. With numerous treatment options available, selecting the right one can be difficult. Dr. Michele Green in NYC is a board-certified dermatologist with over 25 years of experience providing some of the world’s most discerning individuals with the best non-invasive treatment options, including for melasma and hyperpigmentation. When you visit Dr. Green at her private dermatology office in Manhattan’s Upper East Side, she will collaborate with you to create a personalized treatment plan that best suits your needs and aesthetic goals to achieve a more even skin tone and eliminate your melasma once and for all.
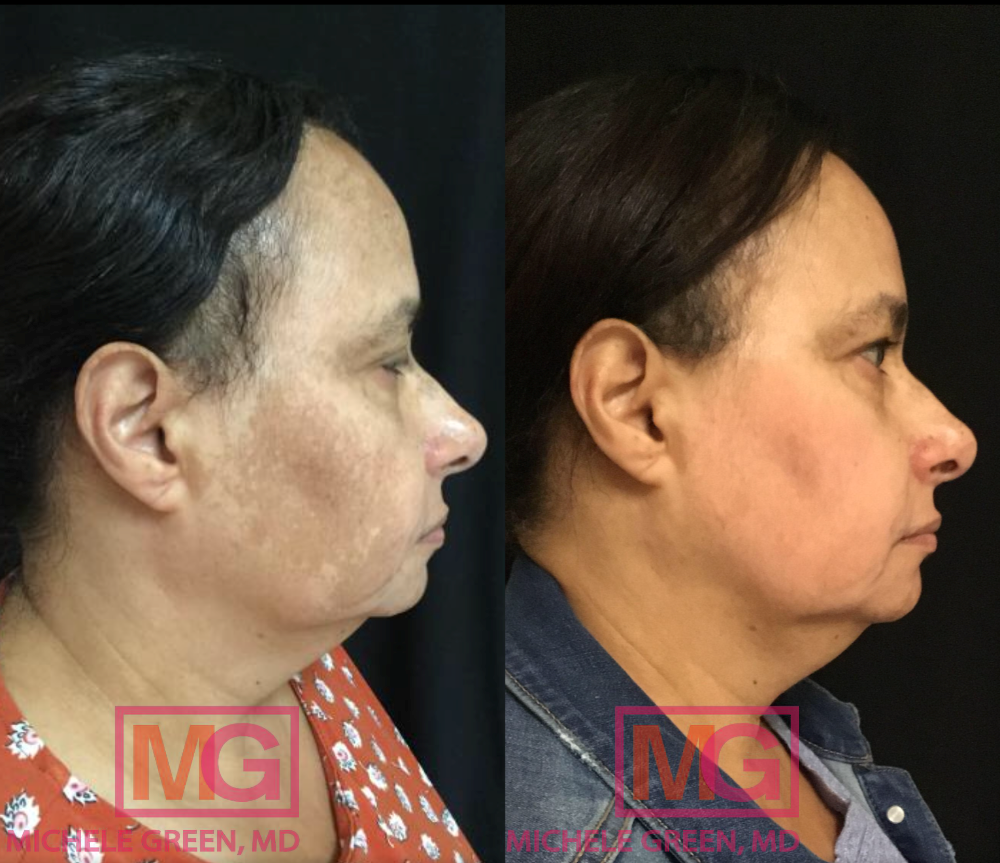
How do I get started with treating my melasma today?
Melasma can be a difficult skin condition to treat and reduce, especially when relying only on over-the-counter skincare products that target dark spots. The most effective way to manage melasma is with a board-certified cosmetic dermatologist, like Dr. Michele Green in NYC, who can create a personalized treatment plan based on your specific needs. They can recommend the best combination of in-office procedures and at-home topical treatments to address your hyperpigmentation. Some of the most effective cosmetic treatments for melasma include Cosmelan peels, Mesopeels, and microneedling, which provide safe and effective options with minimal downtime and no side effects. Whether you’re dealing with melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, sun spots, sun damage, or other types of hyperpigmentation, Dr. Green is here to help.
Dr. Green is a highly acclaimed, board-certified cosmetic dermatologist with over 25 years of experience providing top treatments to some of the world’s most selective clients, including reducing hyperpigmentation and melasma. She adopts a holistic approach and follows a less-is-more philosophy for facial rejuvenation, customizing each patient’s treatment plan to fit their unique needs and aesthetic goals. Dr. Michele Green is frequently recognized as one of NYC’s leading dermatologists by the New York Times, New York Magazine, Super Doctors, and Castle Connolly for her commitment and expertise. When you consult with Dr. Green at her private dermatology practice in Manhattan’s Upper East Side, she will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan aimed at achieving a clear, radiant complexion that lasts. To schedule a consultation with Dr. Green and learn more about the causes of melasma and the best treatment options, please contact us online today or call our New York City-based dermatology office at 212-535-3088.
 212-535-3088
212-535-3088