STD Treatment
Where can I get STD Treatment?
The majority of New York doctors who treat sexually transmitted diseases aren’t particularly concerned with treating the skin-related symptoms of the disease. It can be difficult to find the correct health information, especially about STD treatment. At our private NYC dermatology practice, we prioritize in caring for the the skin care aspect of STD treatment.
If you’re wondering where to get STD treatment please don’t hesitate to contact us online today or call 212-535-3088. Dr. Michele S. Green, a board certified NYC dermatologist, practices the latest techniques at the forefront of skin care to provide the health care level that your skin deserves.
Treatment Options include:
- HPV Treatment – Human papilloma virus, or HPV, causes the appearance of unsightly genital warts that can be removed through one of several treatments offered at our practice.
- Herpes Treatment – Herpes outbreaks can cause a diffuse rash as well as visible sores. The right combination of treatments can help shorten an existing outbreak as well as limit the occurrence of future outbreaks.
- Syphilis Treatment – Syphilis can cause surface symptoms ranging from mild rashes to ulcerative sores. A combination of medications can resolve the disease itself as well as skin problems related to syphilis.
For more information on how to get STD treatment that’s effective, discreet, and incorporates skin care for any visible symptoms, our practice is here to help.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are bacterial, parasitic, or viral infections that can be passed between sexual partners during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Though it can be an uncomfortable health topic for some,it is important to be informed when it comes to preventing and treating the spread of these common infectious diseases. The majority of STDs/STIs are easily treatable, and it is vital to see a doctor for proper STI/STD testing and treatment.
STIs / STDs: Prevention and Testing
For those who are sexually active, the best practice for STI and STD prevention is to practice safe sex, such as using latex condoms, as well as to be regularly tested for STIs/STDs. It is estimated that half of sexually active adults in the United States will be diagnosed with an STI before age 25, so it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about your sexual activity, as well as any symptoms or concerns. Annual STI/STD screening, or testing without clear evidence of symptoms, is recommended for:
- Sexually active women under age 25
- Women over age 25 who are sexually active with multiple sex partners
- Men who have sex with men
- Anyone who is HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) positive
- Anyone who has had unexpected instances of sexual activity
Additional screening is recommended for certain specific STIs/STDs:
- HIV screening: at least once for anyone ages 13-64
- Hepatitis C screening: anyone born between 1945 and 1965
Furthermore, for pregnant women, it is recommended that you be screened for HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Chlamydia, Syphilis, and Gonorrhea. A vaccine is readily available for anyone who tests negative for Hepatitis B to prevent future infection.
What is STD Treatment?
STD treatment varies depending on diagnosis, but the majority of STD treatments involve either oral, topical, or combination medical treatment. If you’re wondering how long STD treatment takes, how to get STD treatment, or about specific medications, you can read below for detailed information on a variety of symptoms.
HPV
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) or condyloma acuminate is the most common STD in New York; approximately 20 million Americans are infected with HPV. An accurate diagnosis and effective treatment for HPV is important, since some strains of the disease can cause cervical and penile cancer. Incorporating skin care with the other recommended treatment guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for the disease can help to keep you healthier.
There are between 30 to 40 different types of HPV, most of which are transmitted via sexual contact. Some forms of HPV cause visible genital warts, while more high-risk strains can progress to precancerous lesions and even cancer. In fact, HPV is responsible for the vast majority of cervical cancer.
Most HPV infections are temporary and don’t have long-term effects; 70 percent of HPV infections resolve without treatment within a year, and 90 percent within two years. In about 10 percent of women, the infection continues and progresses, leading to a higher risk of precancerous lesions and cervical cancer. The good news is that proactive strategies (like yearly Pap exams) are excellent at detecting any abnormal cells before they become cancerous or even precancerous.
The strains of HPV that cause cancer are not the same strains that are responsible for producing genital warts. HPV warts are spread through physical contact, and usually appear as a small bump or groups of bumps in the genital area. They vary in size and shape.
HPV Skin Treatment
Treatment of HPV is very important since some strains can cause penile and cervical cancer. If you’re wondering where to go for STD treatment related to HPV, Dr. Green offers private, discrete, and expert genital wart treatment for rectal, penile, and vaginal warts. Treatment options include topical prescriptions such as Podofilox, electrocaurtery wart removal, and laser surgery to destroy the warts.
Prevention of contracting several strains of HPV can be achieved via the HPV vaccine. If you are between the ages of 9 and 26, you may be eligible for an HPV vaccine.
Herpes
Herpes is a sexually transmitted disease, spread through physical contact and affecting one in six Americans. Herpes can appear anywhere on the skin but usually affects the lips and genital area. As with all sexually transmitted diseases, prompt and accurate diagnosis is an essential part of effective care. At our New York practice, skin care for surface symptoms of herpes is incorporated as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Herpes Simplex is a common viral infection. Herpes is generally categorized into two types: herpes type 1 (HSV-1, or oral herpes) and herpes type 2 (HSV-s, or genital herpes). Most commonly, herpes type 1 causes sores around the mouth and lips. Generally herpes type 2 causes sores around the genitals or rectum.
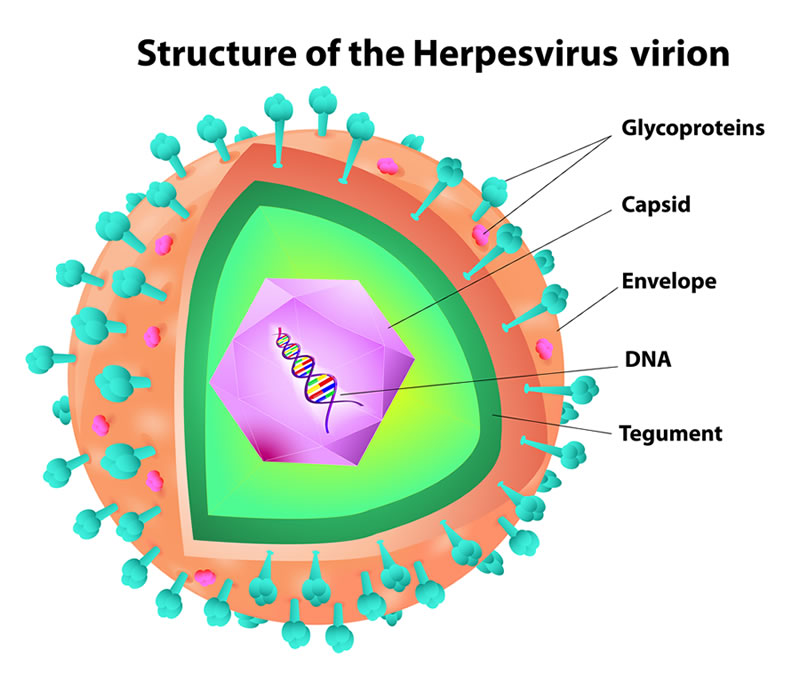
Herpes can be transmitted through oral secretions or sores on the skin. In general, herpes type 2 is spread through sexual contact. Both herpes type 1 and 2 can spread even when the sores are not present. Herpes outbreaks can be brought on by stress, fatigue, general illness, immunosuppression, sun exposure or surgery.
When an individual’s immune system is lowered, herpes outbreaks may more commonly occur. A blood test or culture can be used to diagnose herpes, which the untrained eye often confuses with other skin conditions. If you have or suspect you may have herpes, it’s important to get tested in order to receive proper treatment and take the right precautions with any future sexual partners.
Herpes Skin Treatment
If there is an outbreak, a viral culture or swab of the affected area may be obtained and evaluated in the laboratory. Blood tests can also be helpful in identifying past exposure. Treatment can consist of various antiviral medications in the form of ointments and pills, or a combination of the two. Prescription medications can both prevent the occurrence of the disease or shorten the duration of the outbreak of the infection. Medications may include Valtrex, Zovirax, and Famvir. If outbreaks are frequent, Dr. Green may prescribe suppressive therapy or medications to take regularly in order to prevent these flares from occurring.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a common sexually transmitted disease that usually affects people in New York City under the age of thirty. When a person is infected with syphilis, he or she will develop painless sores that last approximately four to six weeks. Syphilis is caused by a bacterium that is most easily transmitted through sexual contact. Syphilis can also be transmitted during pregnancy or the birthing process from a mother to her fetus.
The disease is broken down into four separate stages, and each stage has its own set of distinct symptoms. The first and second stages of the disease include distinctive skin conditions. In its earliest stage, syphilis will manifest as a single painless skin ulceration that is firm and not itchy. This is known as a chancre. The second stage presents with a diffuse rash through the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
The infected person may experience a loss of appetite, fever, rash, fatigue as well as arthralgias. If left untreated, syphilis can cause long-term damage to the heart, brain, skin, bones and nervous system.
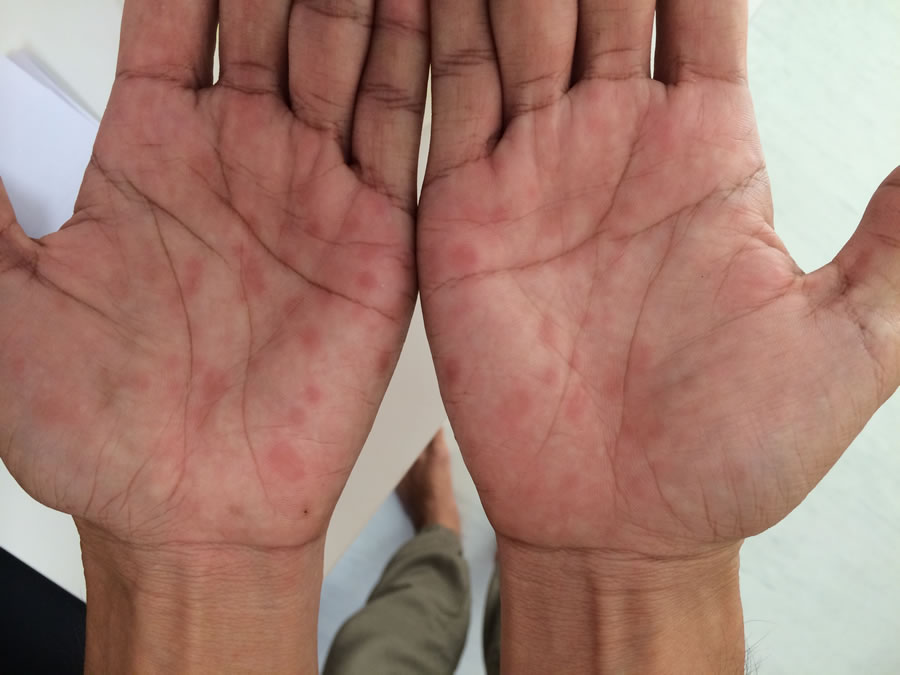
Syphilis Skin Treatment
Antibiotics like penicillin is the preferred and most effective treatment to combat syphilis, and the rates of the disease dropped significantly with the widespread availability of these medications in the 1940s. However, syphilis rates increased again recently at the turn of the millennium, often in combination with HIV infection and/or unsafe sexual practices.
A skin care treatment program that addresses the skin conditions that are commonly associated with syphilis can help minimize permanent damage and help patients feel more comfortable. Dr. Green takes a comprehensive approach toward managing syphilis, addressing not only the underlying cause of the disease with antibiotics but also treating the appearance of surface skin conditions. This combination approach leads to a faster, more comfortable recovery for her patients.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is a common, typically mild, parasitic infection that can affect both men and women. Symptoms can appear anywhere between 5 and 28 days after initial infection, and usually include atypical genital discharge, painful urination, or painful sexual activity. Trichomoniasis can be treated easily with antibiotics, such as metronidazole. However, as the infection can often recur, it is important that all sexual partners be treated before reengaging in sexual activities.
Chlamydia and Gonorrhea
Chlamydia is an extremely common STD that puts the patient at risk for infertility if left untreated. STD symptoms from Chlamydia often go unnoticed, as the severity of symptoms varies widely from person to person. Symptoms can include a burning or itching sensation, painful urination, or atypical discharge, but many patients are asymptomatic.
Similarly, Gonorrhea can go unnoticed in its early phases and can cause infertility. Symptoms of Gonorrhea include painful urination, atypical discharge, pelvic pain in women, and swollen testes in men. Gonorrhea and Chlamydia infections often occur together so, typically, a patient is treated for both if tested positive for one or the other.
Like Syphilis and trichomoniasis, both Chlamydia and Gonorrhea are bacterial STDs, and can often be fully treated with a single dose of antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone, azithromycin, or doxycycline). Chlamydia and Gonorrhea should be treated early on to prevent the development of pelvic inflammatory disease, which can cause infertility in women. If you experience any of the above symptoms, or have a previous sex partner who has tested positive for Chlamydia or Gonorrhea, it’s important to contact a healthcare provider as soon as possible to be tested and begin any necessary STD treatment.
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the STI that causes acquired immune deficiency deficiency syndrome (AIDS). HIV targets and destroys cells within the immune system, which can put HIV positive patients at greater risk for a variety of different health problems. The Department of Health and Human Services has studied the biology, prevention, and treatment of HIV/AIDS, and several treatments have been developed to lessen the severity of HIV/AIDS. A combination of antiviral drugs and antiretroviral therapy can be used to improve the immune system. If you are at high risk for HIV infection, practicing safe sex and a talking to your doctor about preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) can help to prevent future infection.
How much does STD treatment cost?
Cost is a common concern when confronting STI/STD symptoms. You may be wondering, does insurance cover STD treatment? Does medicaid cover STD treatment? If you’re wondering how much STD treatment is, contact the office today to see what treatment your insurance covers.
To learn more about the benefits of incorporating skin care as part of your STD treatment plan, please don’t hesitate to contact us online today or call 212-535-3088. Dr. Michele S. Green, a board certified NYC dermatologist, practices the latest techniques at the forefront of skin care to restore the skin health that you deserve.
 212-535-3088
212-535-3088