Types of Tinea (Capitis, Corporis, Cruris, Versicolor)
What Are The Different Types of Tinea
What are tinea infections? Tinea is a fungal infection of the skin, that is not generally serious and is quite common. Tinea is a type of infectious disease that can be caught from contact with other people, and items and surfaces that they have been in contact with. A common name for some forms of tinea such as tinea corporis, is ringworm, but the name is slightly misleading, since it is not caused by, or involve actual invertebrate worms. Instead, the name derives from the appearance that the infection can display.
Tinea is actually caused by a dermatophyte infection. A dermatophyte is a type of fungus that is able to grow on body surfaces such as the skin and hair. Tinea and dermatophyte infections should not be confused with a different type of fungal infection, Candidiasis. This particular fungal infection is caused by a type of yeast (Candida). Some forms of tinea can be treated with over-the-counter creams and medications.
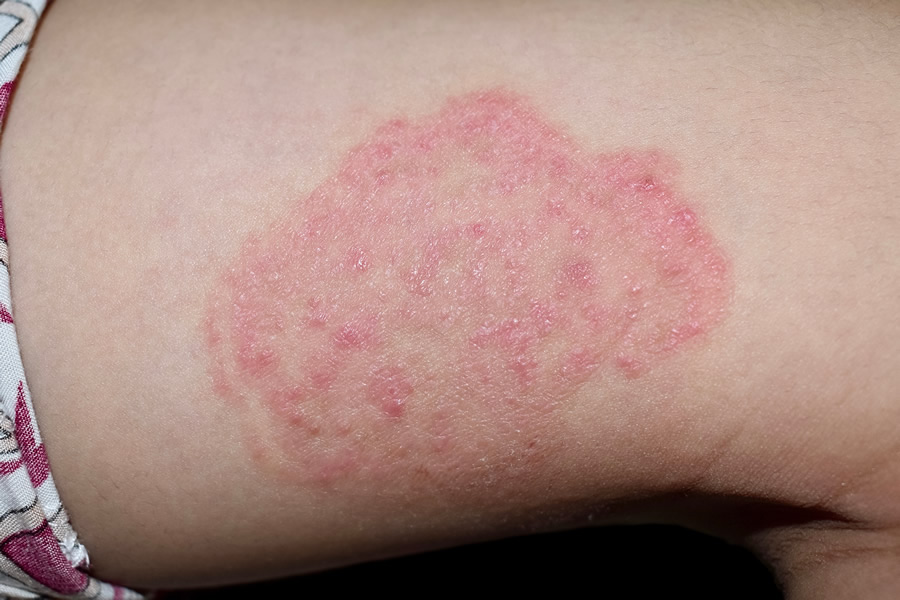
Tinea Corporis (Ringworm)
Tinea corporis (commonly known as ringworm) is a superficial fungal infection (dermatophytosis) which normally occurs on a person’s arms and legs. However, tinea corporis can be found on other areas of the body in some cases. Ultimately tinea corporis is a fungal infection of the skin.
You can typically identify the rash by its appearance, of an enlarged red scaly annular circle, with a central clearing in the middle of the ring. In areas of the body where there is hair, (such as the beard or scalp) there may be a certain amount of hair loss associated with the infection.
Tinea corporis is caused by a fungus known as a dermatophyte. Tinea thrives in moist and humid environments and is typically spread from person to person. It is also possible to catch it via a pet. Direct contact (such as skin-to-skin contact) with an infected person is not necessary. The disease can also be caught from inanimate objects which is the most common cause of tinea infection.
If you suspect that you have tinea corporis then diagnosis is normally made by carrying out a skin examination. Your dermatologist will carry out a scraping of the fungal culture and analyse the results. This can take a few weeks to get a positive result, since it can take a little while to grow the culture in the lab. Occasionally, tinea corporis can be confused with atopic dermatitis (more commonly known as eczema)
The starting point for treating fungal infections such as tinea corporis is to use topical antifungal creams that are applied directly to the affected area. If the tinea infection is serious and widespread over the body then oral medications may be prescribed. If using a topical antifungal cream you should expect to see the infection clear up within a couple of weeks, however it is recommended that you continue using the cream for an additional week to ensure that the fungus is completely removed, since it can linger even when it doesn’t appear on the skin.
Typically in people with a healthy immune system, fungal infections such as tinea should be fairly easy to treat and the fungal skin infection should react well to the medication. There are a number of different topical antifungal creams available, which Dr. Green may prescribe. Some of these include: Clotrimazole, Miconazole, and Ketoconazole. Oral medications, such as griseofulvin and terbinafine when prescribed will need to be taken for a week.
Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm)
Tinea capitis (scalp ringworm) is caused by a superficial fungal infection that affects the scalp. This is commonly caused by the Tichophyton and Microsporum type of dermatophytes fungus.
Visually you can generally identify tinea capitis with patches of hair loss. You will also find some broken hairs and “black dots”. Some find that there will be a range of other issues in the area too, from general inflammation and swelling, to pustules (pus filed spots as you might see with acne), scaling, flaking and itchy skin. The scalp may become red in color and red rings may also appear. For some this may also present itself as dandruff on the scalp (seborrheic dermatitis).
Typically, the best way to treat tinea capitis is to use an oral antifungal medication such as Griseofulvin or Lamisil. To ensure that the treatment is effective, blood and hair cultures are taken to monitor the efficacy of the treatment.
Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch, Groin Ringworm)
Tinea cruris, is a type of tinea that affects the groin area. This type of ringworm is also commonly known as jock itch. This type of tinea infection is more commonly found in men than women, but both sexes can become infected with it. Since tinea cruris likes warm, dark and moist areas, this type of dermatophyte can thrive in the groin area.
It’s common for Tinea to spread to other areas of the body. For example a person who has tinea pedis (athlete’s foot) could also experience a fungal nail infection (tinea unguium) and vice versa.
One type of fungus that can commonly cause tinea cruris is Trichophyton rubrum. However, there are other fungi that can also cause tinea cruris such as: Candida albicans. Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Epidermophyton floccosun.
As with other tinea infections, tinea cruris can be treated with topical antifungal medications such as the azole or allylamine type. These types of anti-fungals stop the organisms from producing ergosterol which in turn stops the fungus from producing a cell wall, which ultimately kills the fungus.
Tinea Versicolor
Tinea versicolor is a long-term (chronic) fungal infection of the skin. It is a relatively common skin infection caused by the yeast Pityrosporum ovale. This condition tends to alter the appearance in of the skin in small dark, patches. You may initially notice a small, dark or discoloured area of skin that can also be scaly. Generally, this condition presents itself on the chest and shoulder area. You may also having an itchy rash.
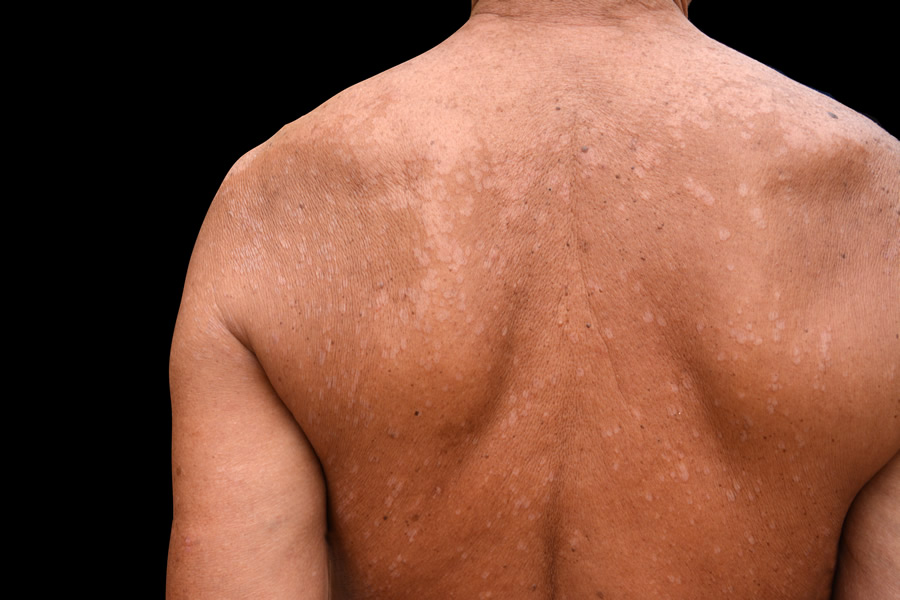
The way tinea versicolor is treated is by applying topical antifungal medications to the infected area on the skin. If this doesn’t clear up the problem, or if the tinea versicolor is a bad case and has spread a lot, then it may be more appropriate to treat the condition with oral anti-fungal medication such as Nizoral.
This is a common condition and occurs especially in warm climates. In warm or humid weather you may find that this condition returns. If this is the case you may be prescribed a medicated cleanser, which can be used to prevent the yeast that causes the condition from overgrowing.
Other Forms of Tinea
There are other forms of tinea that can occur. Modern dermatology treatments such as medications and topical treatments can be used to treat these forms of tinea effectively.
- Tinea Faciei – This is a tinea fungal infection that affects the face.
- Tinea Barbae – This type of tinea is classified as a fungal infection of the hair follicles and often can occur in and around men’s beards.
- Tinea Unguium – (also known as: Onychomycosis) This is a form of tinea that affects the nail. Fungus can grow on the nail and discolor it. Over time the nail can become damaged, can split, and even remove itself from the nail bed.
- Tinea Manuum – This is a tinea infection that is constrained to the hands and fingers.
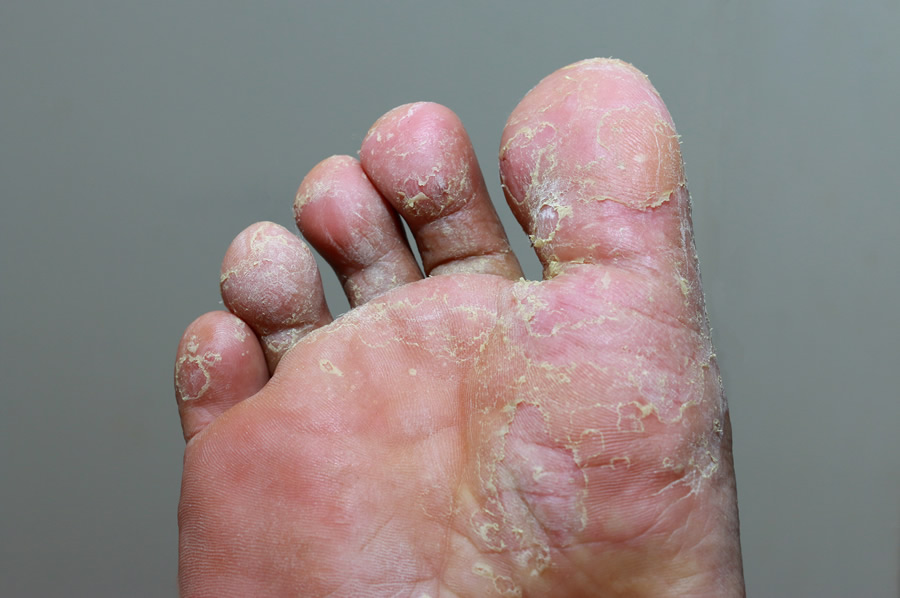
- Tinea Pedis – Tinea infections that affect the feet and foot area.
If you’re concerned about certain skin conditions such as tinea, please don’t hesitate to contact us online today or call 212 535 3088. Dr. Michele S. Green, a board certified NYC dermatologist, practices the latest techniques at the forefront of skin care to give you the look that you deserve.
 212-535-3088
212-535-3088