Hair Shedding vs. Hair Loss
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, more than 80 million Americans experience hair loss or thinning. Regardless of the cause of hair loss, noticing a decrease in hair thickness and density in various areas of the scalp can be extremely distressing for patients, leading to low self-esteem and symptoms of depression. With many treatment options available on the market and varying levels of effectiveness, determining the best way to treat and prevent hair loss can be difficult. Therefore, the best first step toward developing a hair loss treatment plan is to seek out an expert board-certified dermatologist, such as Dr. Michele Green in NYC, who can recommend the most effective treatment option for hair rejuvenation.
When you have your initial consultation with Dr. Green, she will examine the treatment area and run any necessary tests to determine the type of hair loss that is occurring. Some patients may be experiencing hair shedding, which occurs due to an interruption of the hair growth cycle, usually caused by extreme stressors like childbirth, extreme weight loss, surgery, severe illness, or a change in medications. Hair loss, on the other hand, occurs when a factor prevents hair growth from occurring and can be caused by hereditary hair loss conditions like androgenetic alopecia, autoimmune disorders like alopecia areata, or poor hair health associated with tight hairstyles, traction alopecia, or scarring alopecia. By determining the cause, Dr. Green can recommend the best treatment options to meet each patient’s individual needs.
For some patients, the ideal treatment may be a topical solution, such as Rogaine (topical minoxidil) or spironolactone. Oral medications, such as finasteride, can be prescribed by a dermatologist in conjunction with topical treatments. Topical and oral medications can also be paired with in-office treatments like platelet-rich plasma injections (PRP), stem cell therapy, or low-level laser therapy to strengthen the hair follicles, enhance blood flow, and promote new hair growth. Dr. Green can also recommend the best hair products, including shampoos, serums, supplements, and conditioners, that will help prevent additional hair shedding or thinning. To embark on your hair care and regrowth journey, schedule your initial consultation with Dr. Michele Green.
Experienced board-certified dermatologist Dr. Michele Green has been expertly treating patients at her Upper East Side, New York City dermatology office for more than 25 years. Well-versed in addressing a wide range of cosmetic concerns and medical conditions, Dr. Green is a master at identifying the root cause of hair loss to create an individualized treatment plan that will slow hair shedding and strengthen hair follicles for thicker hair regrowth. In addition to hair loss treatment, Dr. Green is an expert in cosmetic treatments such as Botox, dermal fillers, laser therapy, microneedling, chemical peels, platelet-rich plasma injections, and more. Well-known for high patient satisfaction, Dr. Green has been voted one of the best dermatologists in New York City by such publications as Castle Connolly, Super Doctors, and New York Magazine.
Does hair fall out / shed naturally? What is excessive hair shedding vs. normal hair shedding?
Hair shedding is a natural part of the hair growth cycle, which is composed of three major steps: the anagen phase (growth phase), telogen phase (resting phase), and exogen phase (shedding phase). The growth phase lasts for 2-7 years, and about 80% of the hair on our heads is in the growth phase at any given time. Once the hair is done growing, it enters the catagen phase (transition phase) into the resting phase, which lasts for approximately three months. After the resting phase, there is the shedding phase, which involves the hair falling out naturally. On average, people lose 50-100 strands of hair a day due to shedding. However, excessive shedding occurs when more than 100 hairs fall out a day, and can be caused by many potential factors, including extreme stress, thyroid conditions, and recovery from childbirth, surgery, or major illness. Excessive hair shedding typically occurs 2-6 months after the stressful event.
When is hair shedding hair loss?
Hair shedding occurs when patients lose more than 50-100 strands of hair per day, and is caused by a stressful event that triggers the hair follicles to enter the resting phase (telogen phase) early, which is a common cause of hair loss. Medically, this is a condition known as telogen effluvium. After the stressful event has resolved, the normal hair cycle should resume, providing patients with a full head of hair again. Hair loss (anagen effluvium) occurs when the hair follicle is damaged, preventing new hair growth, and can be caused by several factors, including hormonal imbalances (pregnancy or menopause), genetic predisposition (male and female pattern hair loss), immune system health conditions, and repeated friction. Depending on the extent of the damage, hair loss conditions may result in a decrease in hair density or permanent hair loss.
What are the different types of hair loss?
The most important step in beginning hair loss treatment is receiving an accurate diagnosis of the root cause of the hair loss. Hair shedding and thinning can occur due to genetic predisposition, stress, autoimmune system disorders, thyroid problems, cancer treatment, hormonal changes, or as a side effect of some medications. Below are some of the most common conditions that lead to bald spots, hair loss, or rapid hair shedding:
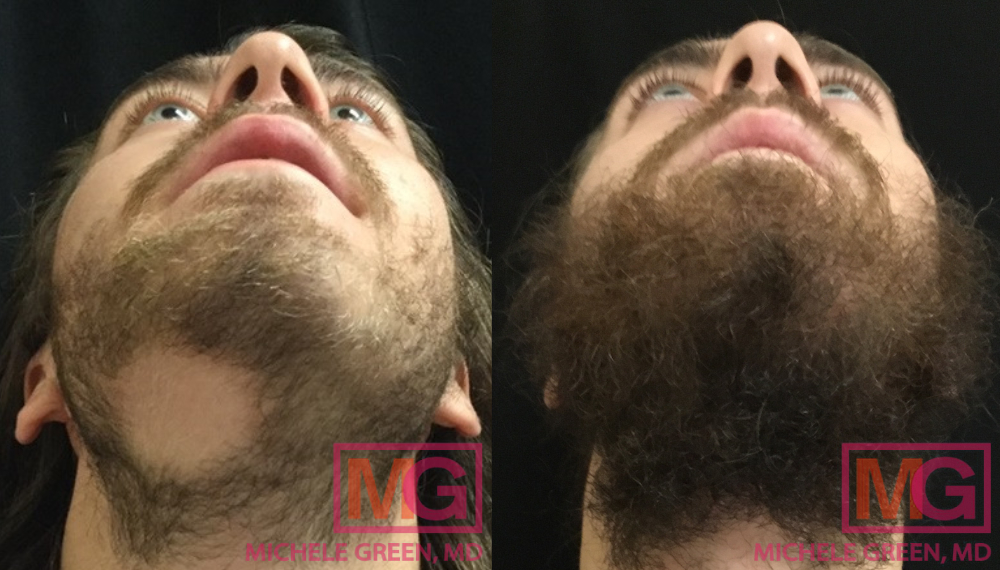

Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as female or male pattern baldness, is a hair loss condition associated with elevated levels of the androgen hormones, which bind to the hair follicles and damage them. In men, male pattern hair loss typically begins with hair thinning at the temples, resulting in a receding hairline that creates the characteristic “M” shape. Hair loss continues on the crown of the head and can continue to worsen over time. In women, thinning hair typically begins along the top of the head, causing the hairline to widen. The condition can begin affecting both men and women in their 20s and 30s and can become more prominent with age. The risk factors for developing androgenetic alopecia are yet unknown, though researchers believe that there is a strong genetic component.
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a hair loss condition caused by extreme stress or shock, which triggers hair to enter the resting phase of hair growth (known as the telogen phase) prematurely. As a result, a large number of hairs enter the shedding phase at the same time — sometimes, as many as 70% of the hairs on the scalp can be shed at once, leading to noticeable hair thinning and shedding. Stressful events that can trigger telogen effluvium include:
- Severe illness, such as chronic illness or high fever
- Childbirth
- Overactive thyroid
- Severe infections
- Severe psychological distress
- Major surgery or injury
- Losing weight quickly, such as crash diets or anorexia
- Some medications
Typically, hair will regrow in three to six months once the stressful event has been resolved, but seeking treatment from a dermatologist can help speed up the regrowth process and ensure the overall sound health of the hair follicles.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that occurs when white blood cells damage the hair follicle, causing new hair growth to slow and the follicle to shrink. Characterized by bald patches that appear most commonly on the head (though the condition can develop anywhere on the body), alopecia areata can occur suddenly. However, it is not associated with stress-related situations. Researchers believe that the condition is genetic, and while some patients can experience alopecia areata followed by full hair regrowth, for some, hair loss may be permanent. For the most part, patients with alopecia areata experience small patches of hair loss the size of a quarter. However, for others, the extent of hair loss may be more extreme. Alopecia areata can affect patients of any age and gender and frequently comes on quickly, within the span of a few days.
Is my hair shedding or falling out?
The first step to treating hair loss is to schedule a consultation appointment with a dermatologist, such as board-certified dermatologist Dr. Michele Green. Dr. Green will ask you to disclose your medical history and then run tests to diagnose the type of hair loss you are experiencing. Once the cause of hair loss is determined, Dr. Green will generate an individualized treatment plan to strengthen the hair follicles, promote hair regrowth, and slow the loss of hair. It is essential to seek treatment from a dermatologist, as purchasing over-the-counter medications without consulting an expert can result in a worsening of the condition.

Can hair loss be prevented?
Hair loss and hair thinning are very common conditions affecting as many as 50 million men and 30 million women, and as such, many treatment options are available—some more effective than others. The most effective treatment, however, is the one that works to address your specific cause of hair loss. Depending on the type of hair loss occurring, Dr. Green may recommend prescription medication, such as topical minoxidil (Rogaine), finasteride (Propecia), or spironolactone (Aldactone), an in-office treatment such as PRP injections, low-level laser therapy (LLLT), or lifestyle changes, such as increasing intake of vitamins like biotin and improving your hair care routine for strong, healthy hair.
Minoxidil for hair loss treatment
Minoxidil was originally prescribed to treat high blood pressure but has since been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for hair loss when applied topically or taken orally to help stimulate new hair growth and maintain the health of hair follicles. The only FDA-approved over-the-counter (OTC) medication for hair loss, minoxidil is known as a vasodilator, meaning that when it is applied to the scalp, it widens the blood vessels for increased blood flow to the area. This helps to raise oxygen levels to lengthen the hair growth phase and triggers dormant hairs to grow again. Additionally, minoxidil has anti-inflammatory properties, meaning that it can block androgens, such as DHT, which bind to hair follicles and cause damage. One of the possible side effects of the topical treatment is scalp irritation. Patients experiencing scalp irritation may be prescribed oral minoxidil instead.
PRP injections for hair loss treatment
PRP for hair loss works through the injection of the high platelet count plasma found in the patient’s blood into the area of the scalp where hair loss is beginning to show. This platelet-rich plasma works to activate proteins in the body called “growth factors,” which serve a variety of helpful purposes. When it comes to the prevention of hair loss, growth factors can work to improve circulation in the treatment area, which can help to thicken the hair follicle. As a result, the new hair growth at the injection site is thicker and healthier looking. Furthermore, these growth factors can help to heal and reactivate hair follicles, increasing hair count in the area. The proteins also work to stimulate the papilla cells, which help to promote new hair growth. Altogether, this means that PRP treatment works to strengthen the hair follicle for thicker hair and activate previously inactive hair follicles for new growth, which serves to counteract hair loss.
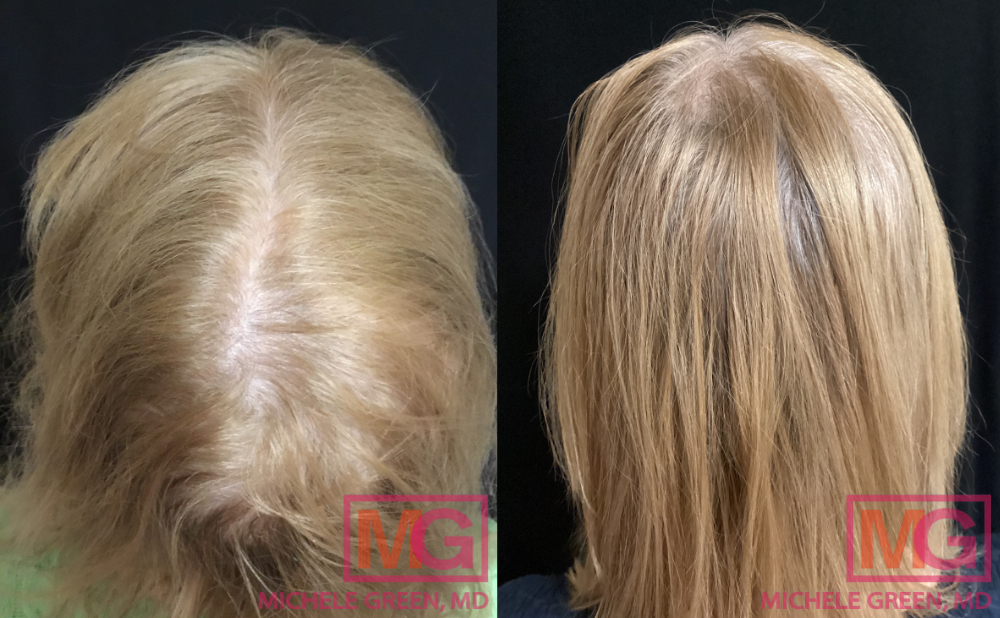
Finasteride for hair loss treatment
Finasteride is the generic term for the drug Propecia, which can be used to address male pattern baldness and hair loss. One contributing factor to androgenic alopecia is the binding of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) androgen to hair follicles, which damages the follicle and leads to hair thinning and hair loss. Finasteride is a DHT blocker, meaning that it inhibits the conversion of testosterone into DHT, reducing hair loss. Dr. Green may prescribe finasteride paired with minoxidil for the best results. According to a study published in the Journal of Dermatologic Therapy, 94% of men in the study experienced an improvement in their hair loss condition with minoxidil and finasteride combined.
Hair loss vs hair shedding FAQs
How much hair loss is normal in the shower?
Hair shedding is a natural part of the hair growth process, so it is normal for people to lose some amount of hair in the shower, specifically, 50-100 strands of hair a day. Losing hair can be particularly noticeable in the shower when you wash and condition your hair. If you notice some hair in your drain after a shower, that is normal and nothing to worry about. However, suppose you notice your hair coming away in clumps when you wash or condition your hair. In that case, it is best to schedule a consultation appointment with Dr. Green to discuss the underlying cause of excessive shedding.
What does it mean if your hair is falling out?
Patients often ask, “What does it mean when your hair falls out a lot?” Several types of hair loss conditions can lead to sudden hair loss, including Alopecia Areata, Telogen Effluvium, and Anagen Effluvium. Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissue, including the hair follicles. This damage to the hair follicles can lead to bald patches, thinning hair, and slowed hair growth. Alopecia Areata is a genetic condition that can progress to complete hair loss. Telogen Effluvium is another sudden hair loss condition that is caused by a stress-based event, such as severe illness, injury, surgery, or childbirth. The condition causes between 20 and 50% of the hair follicles to enter the resting phase at the same time, leading these hairs to shed about three months later. Typically, telogen effluvium is an acute condition, and the hair will grow back after six months if the stress is removed.
What does it mean when your hair is shedding?
Patients will often wonder, “What does it mean when your hair sheds a lot?” When you notice your hair shedding a lot, it is important to consult with an expert dermatologist, such as Dr. Green, to determine the underlying cause of the hair loss. Hair shedding can occur due to damage caused by heat styling, scalp irritation, hair breakage, or a stressful event like childbirth, severe illness, or surgery. To find the best treatment option, it is essential to diagnose the root cause of the hair loss. Dr. Green has many treatment options available that may help your hair grow back and prevent severe hair loss in the future.
Can anesthesia make your hair fall out?
Surgery is a stressful event that may trigger telogen effluvium, which is acute hair loss that occurs when your body shifts many hair follicles from the growing phase to the resting phase. In addition to the stress of an injury or surgery, research performed in 2023 has revealed that anesthesia can also contribute to hair loss or hair shedding. One study showed that patients who received general anesthesia for surgery were more likely to develop an autoimmune hair loss condition, such as alopecia areata, than those who did not receive anesthesia.
Can biotin make your hair fall out?
Biotin, which is also known as vitamin B7, is a nutrient that helps with hair growth, along with other nutrients like iron, zinc, and protein. Low levels of biotin may contribute to poor hair health, and patients may notice an increase in hair breakage or shedding. During a stressful event, the body will naturally divert nutrients like biotin, iron, and zinc away from the hair follicles, which can exacerbate hair shedding. Patients can help improve hair health by consuming foods rich in biotin, such as egg yolks, avocados, salmon, nuts, seeds, and legumes.
Does thyroid make your hair fall out?
Thyroid health conditions can contribute to hair loss. Hair shedding due to thyroid problems is often characterized by loss that occurs across the entire scalp rather than in one specific area. The best way to address hair loss caused by thyroid problems is to address the underlying health condition. A mild thyroid condition does not usually trigger hair loss, so patients experiencing widespread hair thinning on the scalp due to thyroid problems will typically require medication for their condition.
Can anxiety make your hair fall out?
Stress and anxiety are major contributors to hair loss and hair shedding. Cortisol is a hormone that is released during both short-term and long-term mental, physical, or emotional stress. High levels of cortisol can interfere with the normal activity of the hair follicles, causing hair loss. While the hair will typically grow back normally after the stress is resolved, patients dealing with chronic anxiety may experience a more prolonged hair loss. The best way to prevent hair loss due to stress is to address the underlying anxiety.
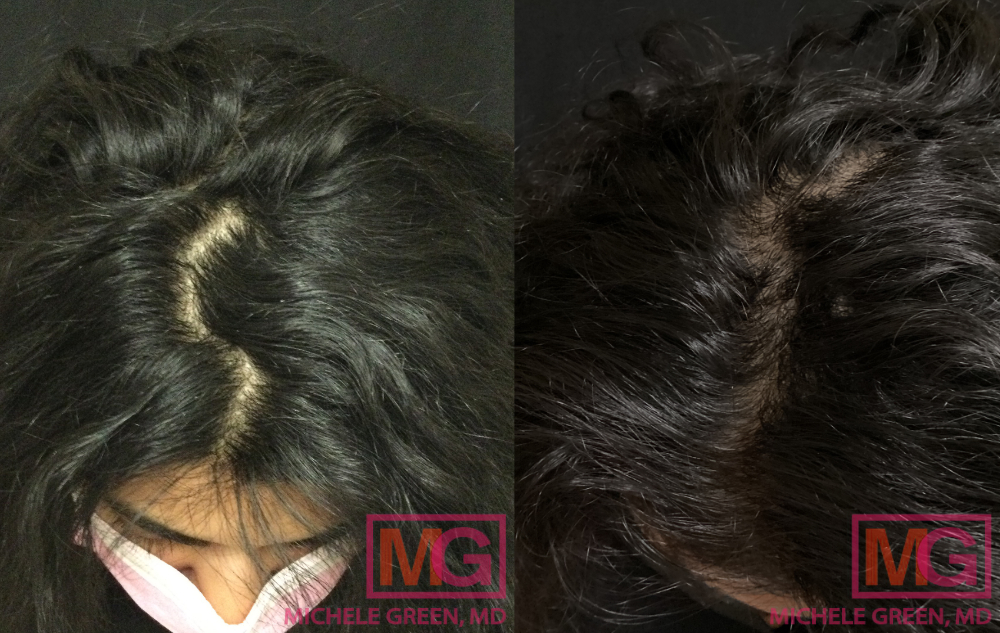
Does hair fall out or shed due to stress?
Patients often wonder, “Can your hair fall out from stress?” Several types of hair loss may occur due to high levels of stress:
Telogen Effluvium is a hair loss condition that occurs when a stressful event causes the hair follicles to enter the resting phase early. Typically, only 15% of the hair follicles can be found in the resting phase at a time. When telogen effluvium occurs, as many as 30% of the hair follicles are in the resting phase, meaning that 2-6 months after the stressful event, a higher-than-typical volume of hair will begin shedding. Patients with telogen effluvium typically see their hair regrow normally, provided the stressful event has been resolved.
Trichotillomania is a condition in which patients have the uncontrollable urge to pull out their hair. Typically, patients affected by trichotillomania will pull out hair on the scalp, eyebrows, or eyelashes. Hair pulling tends to occur when patients feel stressed, lonely, bored, frustrated, or uncomfortable.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that is characterized by sudden hair loss. Several risk factors may contribute to alopecia areata, including stress. Alopecia areata may result in permanent hair loss, meaning the best treatment option is surgical, such as a hair transplant.
Does hair shed more in the winter?
Different weather conditions can contribute to hair loss, and some patients may experience more hair loss in the winter. Cold, dry temperatures outside mixed with hot, dry temperatures inside can contribute to dryness and irritation on the scalp. Dry hair is more prone to breakage, which results in more hair loss. To prevent hair loss in the winter, patients should drink plenty of water, keep their hair moisturized, and try to avoid over-washing, which can further dry out the scalp.
Does your hair fall out more in the summer?
Some patients may experience a greater incidence of hair loss in the summer months. Due to heat and sweat, many people will wash their hair more, which can also irritate the scalp and lead to increased hair shedding. UV rays from the sun can also damage the hair, leading to weaker hair follicles and more breakage. To prevent hair loss in the summer, patients can practice UV protection by wearing a hat lined with silk or satin, which reduces friction.
Does hair shed more in the fall?
Seasonal shedding can also occur for patients in the fall. For some, hair loss that occurs in the fall may be due to hair entering the resting phase during the summer months and shedding during the fall months. In some cases, the changing daylight levels and seasonal hormonal changes can lead to increased shedding. The best way to prevent shedding in any season is to stay hydrated, eat a balanced diet, reduce stress whenever possible, wear your hair in loose hairstyles (rather than tight hairstyles), and avoid heat styling.
Does longer hair fall out more?
It is a common misconception that longer hair falls out more. In fact, longer hair falls out at the same rate as shorter hair. However, it is often more noticeable for patients when longer hair falls out, since longer hair is more likely to clog the drain, linger on your clothing, or get caught on your pillow.
How to get started with hair shedding and hair loss treatment today
Hair loss is extremely common, affecting as many as 80 million Americans. But even so, hair loss can be very distressing, causing patients to feel increased anxiety or lower self-esteem, leading many to seek a solution. With many hair loss treatments available over the counter or advertised by companies like “Hims,” it can be difficult to know which option is the safest and most effective. Additionally, using the wrong product can worsen hair loss and damage to the hair follicles. That is why it is essential to seek treatment from an expert board-certified dermatologist, such as Dr. Michele Green, who has been treating patients in her New York City dermatology office for more than 25 years. Dr. Green makes a full examination of the skin, scalp, hair, and nails to determine the root cause of hair loss and provide a treatment plan tailored to meet patients’ needs.
Dr. Michele Green is an internationally renowned board-certified dermatologist with over two and a half decades of experience providing her patients with the best non-invasive treatment options. Dr. Green takes a holistic approach and embraces a less-is-more philosophy, creating customized skincare routines and treatment plans that cater to the unique concerns and aesthetic goals of her patients. She is consistently identified as one of New York’s best dermatologists by Castle Connolly, New York Magazine, and Super Doctors for her dedication to her patients and expertise. Please call us at 212-535-3088 or email our New York City-based office today to schedule a consultation with Dr. Michele Green and get started on addressing your hair loss today.
 212-535-3088
212-535-3088